Shocking Discovery: Plaque Psoriasis Treatment Linked to Rare NTM Pulmonary Disease
2025-01-20
Author: Sarah
In a world where antibiotics are becoming less effective against increasing rates of antibiotic resistance, non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) present a concerning threat, especially for susceptible patients. Recent studies have highlighted a worrying prevalence of NTM infections, particularly with strains like the Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), which takes the top spot among other species such as M. abscessus and M. fortuitum. Unlike traditional infections, NTM is believed to spread primarily through environmental factors instead of direct human contact, making it a silent yet looming risk in certain lifestyles.
Case Report Overview
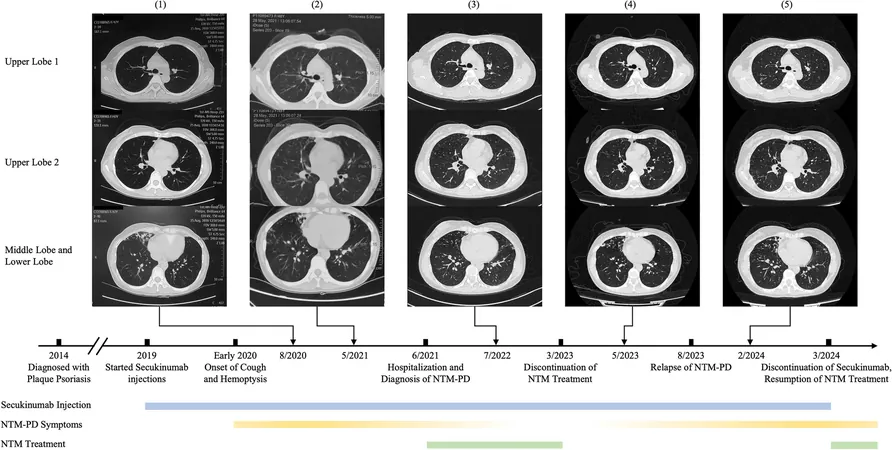
A new case report sheds light on this troubling intersection of plaque psoriasis and NTM pulmonary disease, centering around a 48-year-old woman who developed recurrent NTM disease despite diligent efforts to avoid risk factors, including exposure to hot springs. This patient, who was treated with Secukinumab—an interleukin-17A (IL-17A) inhibitor designed for chronic inflammatory conditions—experienced a persistent cough for over a year before finally receiving a diagnosis correlating her lung issues with MAC infection.
Timeline of Illness
The timeline of her illness began in June 2021, when she was admitted to the hospital due to worsening respiratory symptoms. Initial tests revealed bronchiectasis (BE), a condition that aggravates the susceptibility to infections. Despite treatment with antibiotics providing short-term relief, her lung condition continued to deteriorate. A bronchoscopy, conducted two weeks into her hospital stay, confirmed the presence of MAC via advanced metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS).
Subsequent Treatment and Recurrence
After being put on an NTM treatment regimen and showing promising adherence to her medications, the patient was symptom-free for 20 months. Yet, in August 2023, she experienced a sudden recurrence marked by alarming hemoptysis, leading to further evaluations that again indicated MAC infection.
Implications of Secukinumab Therapy
Intriguingly, the patient's medical journey reveals that she had begun treatment with Secukinumab in 2019. As her psoriasis worsened, the frequency of her injections increased. However, the therapy's immunosuppressive effects—in tandem with her consistent exposure to non-chlorinated hot spring water—might have heightened her susceptibility to NTM infections. This case stands as the first reported incidence linking Secukinumab to such a serious pulmonary condition, casting a spotlight on the potential risks associated with biologics in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Research and Medical Implications
The case not only emphasizes the patient's challenges but also raises crucial questions about the long-term implications of using therapies that can potentially suppress immune function. The complex relationship between bronchiectasis and NTM pulmonary disease suggests that each may exacerbate symptoms of the other—leading us to consider that NTM was a contributing factor to her bronchiectasis, rather than a mere consequence.
Conclusion and Recommendations
As we move forward, it is evident that further research is imperative. The nuances of how immunosuppressive treatments like Secukinumab influence the risk of developing opportunistic infections, particularly NTM, demand greater scrutiny by medical professionals. The implications of this case could inform guidelines for treating patients with immune modulators, ensuring that their therapies do not inadvertently expose them to unanticipated and severe infections.
In conclusion, while treatments like Secukinumab are heralded as advancements in managing chronic inflammatory conditions, this sobering case serves as a critical reminder of the potential offline consequences. Vigilance in monitoring respiratory health and a proactive approach are essential for patients undergoing similar therapies. As we advance in our understanding of NTM diseases and the role of immunomodulatory treatments, comprehensive preventive care could spell the difference between recovery and a life-altering health crisis.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)