Shocking Discovery: Genetic Mutations Unravel Secrets Behind Pulmonary Fibrosis!
2025-09-18
Author: Rajesh
A Groundbreaking Finding from Cancer Researchers!
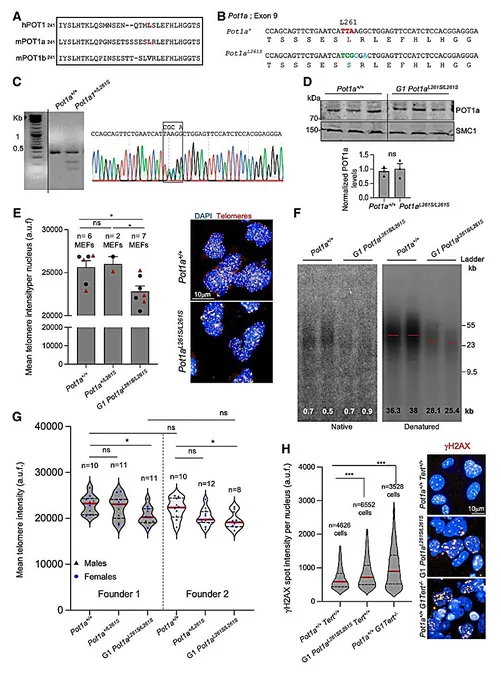
A research team from the National Cancer Research Center (CNIO) has made a crucial discovery linking genetic mutations in the POT1 gene to the devastating effects of pulmonary fibrosis, a condition where lung tissue becomes scarred and rigid, making breathing a challenge. This mutation disrupts the crucial repair mechanisms of telomeres, the protective caps on chromosomes.
What is Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a severe disease with no current cure, characterized by scarring in the lungs that exacerbates over time. The disease's molecular mechanisms remain shrouded in mystery, driving scientists to explore its underlying causes actively.
The Telomere Connection!
Pulmonary fibrosis is now known to be tightly linked to dysfunctional telomeres—structures that safeguard our chromosomes. Recent findings by the CNIO have further illuminated this connection, enhancing hopes for effective therapies.
Unlocking the Mutation's Mystery!
The study reveals that a mutation in the POT1 gene—a key player in telomere protection—hinders the repair of telomeres. Maria Blasco, the research lead, emphasized, "This mutation effectively shuts down telomerase, the enzyme responsible for telomere repair, leading to shortened telomeres and, ultimately, pulmonary fibrosis."
The Role of Shelterins in Lung Health!
Shelterins, the proteins formed by POT1, provide a critical shield for telomeres. Our telomeres naturally shorten over time due to cell division. When they become too short, cell division halts, preventing tissue regeneration. In the lungs, this inefficiency can trigger fibrosis.
Reversing the Damage!
Past research from Blasco's team demonstrated that activating telomerase in affected tissues could potentially reverse fibrosis in animals. However, the new study indicates that when the protective shelterin protein POT1 mutates, telomeres remain unrepaired regardless of telomerase presence, leading to inevitable fibrosis.
A Dual Threat: Cancer and Aging!
Previously, mutations in the POT1 gene were exclusive to cancer research, but intriguingly, this discovery marks the first association with a degenerative disease like pulmonary fibrosis. Blasco asserts, "These findings highlight the dual role of POT1 and telomeres in both cancer and aging, emphasizing their critical importance across various diseases."
Towards Personalized Therapies!
As researchers delve deeper into the effects of mutations like POT1, the potential for personalized therapies for telomere-related diseases grows. This exciting breakthrough could pave the way for innovative treatments for not just pulmonary fibrosis, but also various cancer types linked to telomere dysfunction.
Stay tuned as science unravels these mysteries, offering hope for patients suffering from this life-altering condition!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)