Shocking Discovery: Fat in Muscles Heightens Heart Disease Risk – Even for Those Who Are Slim!
2025-01-23
Author: Yu
Introduction
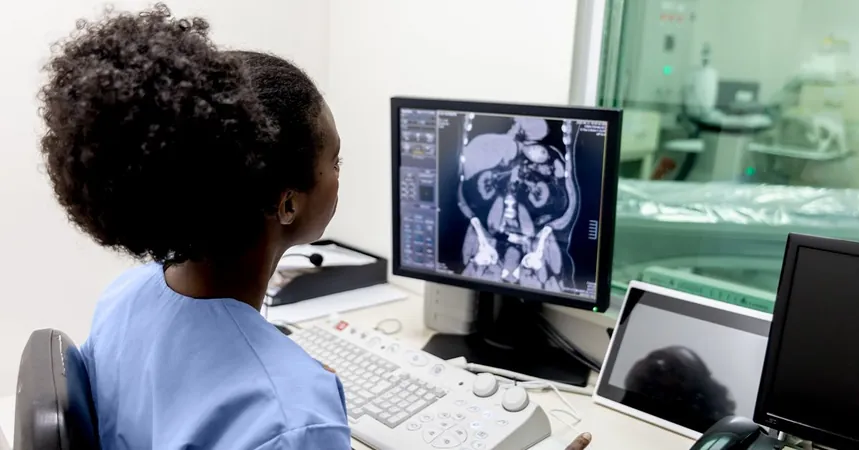
Heart disease continues to reign as the leading cause of death in the United States, claiming the lives of one in five individuals. Worryingly, the threat of this ailment isn't solely confined to those carrying excess weight. Recent studies have unveiled that even individuals of a healthy weight can be at risk due to the distribution of fat in their bodies.
Groundbreaking Research
In groundbreaking research from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, scientists have identified a significant link between intramuscular fat—fat that collects within muscle tissue—and an increased probability of serious heart disease, independent of other known risk factors like body mass index (BMI). The findings, published in the European Heart Journal, suggest that how fat is stored is just as crucial as the amount of fat one carries.
Expert Insight
Dr. Cheng-Han Chen, a prominent interventional cardiologist not involved in the study, emphasized the importance of these findings: "This research indicates that examining fat distribution may offer a more refined insight into an individual’s health than traditional BMI metrics," he noted. This is a revolutionary perspective in heart disease assessment, which could reshape how healthcare professionals evaluate cardiovascular health.
Study Details
The study included a diverse group of 669 participants, predominantly older adults who experienced symptoms linked to cardiac ischemia but had no documented coronary artery disease. Advanced imaging techniques like cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT) scans were employed to analyze heart function alongside fat and muscle composition.
Findings
Researchers specifically focused on the "fatty muscle fraction," quantifying the ratio of intramuscular fat to total muscle and fat. The results were alarming: participants with higher levels of intramuscular fat not only displayed abnormal blood flow in the coronary microvessels but also had an elevated risk of hospitalization, heart attacks, and even death attributed to heart-related issues.
Risk Factors
Just a small increase in fatty muscle fraction could escalate the risk of heart disease significantly—every 1% increase corresponded to a 2% rise in coronary microvascular dysfunction risk and a staggering 7% increment in future serious heart disease risk. These findings echo a vital message: even if you’re maintaining a healthy weight, your muscle composition matters immensely.
Future Implications
Lead researcher Dr. Viviany Taqueti highlighted the implications for future health strategies, recommending that better diagnostics for intramuscular fat could aid in identifying high-risk individuals. "This is a crucial step towards understanding how muscle fat impacts heart health, especially in light of new therapies targeting body composition," she explained.
Connection to Metabolic Disorders
Adding to the intrigue, there might be an intersection between intramuscular fat and metabolic disorders, like insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, hinting that fat stored within muscles may trigger inflammatory processes that could subsequently disrupt normal vascular functions.
A Call to Action
Health officials and cardiologists are now urged to reconsider traditional assessments of heart disease risk, advocating for a broader approach that includes an examination of fat distribution in muscles. As research continues to evolve, it is essential for everyone—regardless of weight—to understand the potential risks tied to muscle fat. This newfound awareness might just be the key to preventing heart disease and ensuring a healthier future.
Conclusion
In the battle against heart disease, awareness is power. Are you at risk? It's time to take charge of your heart health!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)