
Shocking Discovery: Cosmic Megajets Could Spell Disaster for Earth’s Future!
2025-03-24
Author: Ming
Introduction
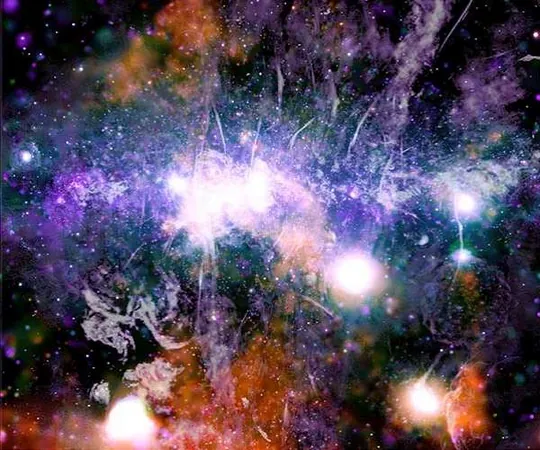
In a groundbreaking revelation that has sent ripples through the astronomical community, researchers have unveiled a potential cosmic threat lurking within the depths of the Milky Way. This alarming discovery stems from a study led by astronomers at CHRIST University in Bangalore, who have identified a colossal spiral galaxy nearly one billion light-years away, featuring a supermassive black hole billions of times the mass of our Sun. This black hole is ejecting immense radiation jets that stretch across six million light-years, marking them as some of the longest jets ever recorded in spiral galaxies.
Challenging Conventional Wisdom
This extraordinary find challenges conventional wisdom, as scientists have traditionally associated such massive jets with elliptical galaxies, not spirals. The implications of this anomaly could force scientists to rethink existing models of galactic evolution and consider the future of galaxies like our own Milky Way.
Significance of the Study
Professor Joydeep Bagchi, the study's lead author, emphasizes the significance of this research: “We must reconsider how galaxies evolve and how supermassive black holes grow within them. If spiral galaxies can not only survive but also flourish under extreme conditions, what does that mean for our Milky Way? Could we see similar high-energy phenomena that could endanger life on Earth?”
Galaxy 2MASX J23453268-0449256
Published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, the research highlights the galaxy identified as 2MASX J23453268-0449256, which dwarfs the Milky Way in size, being roughly three times larger. Utilizing data from esteemed telescopes, including the Hubble Space Telescope and the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope, researchers traced the origins and vast reach of this galaxy's incredible radio jets.
Surprising Order Amidst Energy Output
Surprisingly, even with such vigorous activity from its supermassive black hole, the galaxy retains an orderly spiral structure complete with luminous spiral arms and a stable ring of stars, contradicting prior assumptions that such energy output would lead to disorder.
The Hot Gas Halo
Adding to the intrigue is the hot gas halo surrounding the black hole, which emits X-rays. This gas, while cooling down, is reheated by the black hole's jets, thereby halting new star formation despite a substantial supply of raw materials—a perplexing phenomenon that scientists are keen to understand further.
Potential Threat to the Milky Way
Currently, the Milky Way's black hole, Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), is in a relatively quiescent state, weighed down at four million solar masses. However, an encounter with surrounding matter, such as gas clouds or smaller galaxies, could trigger similar jet activity here. Historical records from other galaxies suggest that such Tidal Disruption Events (TDEs) are plausible and could occur in our galaxy, raising concerns about the potential for catastrophic jets as a future hazard.
Severe Ramifications for Earth
The ramifications for Earth could be severe. High-energy jets from our own galaxy could strip away planetary atmospheres, disrupt existing DNA structures, and drastically increase mutation rates. Direct exposure to these jets could even erode the ozone layer, leading to potential mass extinction events. On a larger scale, such jets could fundamentally alter the interstellar medium, impacting star formation and galactic structure.
Dark Matter and Galaxy Stability
Moreover, the study revealed that the galaxy J23453268-0449256 possesses ten times more dark matter than the Milky Way, assisting in the stabilization of its rapidly rotating disk—a key factor for its prolonged resilience under extreme galactic conditions.
Broader Implications of Findings
Co-author Shankar Ray, a PhD candidate, notes the broader implications of their findings: “By understanding these unique galaxies, we can gain crucial insights into the forces that shape the universe, including dark matter, the evolutionary fate of galaxies, and even the origins of life itself. This research brings us closer to unraveling cosmic mysteries that continue to fascinate humanity.”
Conclusion
As scientists delve deeper into understanding the phenomena at work within these colossal galaxies, the potential implications for our own Milky Way—and indeed, life on Earth—are profound and underscore the importance of further astronomical exploration. Buckle up, because the cosmos might just have more surprises in store that could alter our very existence!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)