Shocking Discovery: A Rare Case of Skin Cancer in a Sun-Protected Area Raises Alarm for Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis Patients!
2025-04-03
Author: Siti
What Is Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis?
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is a rare genetic disorder that severely compromises the skin's immunity against specific strains of beta-human papillomavirus (HPV). Patients with EV are at a heightened risk for developing various skin lesions, and notably, many cases of SCC correlate directly with sun exposure. However, this recent report has turned that assumption on its head, revealing how a covered area of the scalp can also become a site for malignant transformation.
The Case That Shook the Medical Community
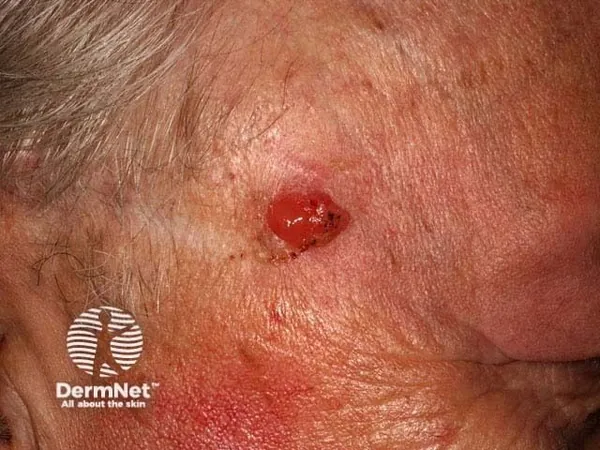
The case revolves around a 28-year-old Palestinian woman whose struggle with EV began as a teenager, manifesting in wart-like lesions across her face, scalp, and other parts of her body. Despite having adhered to sun-protective measures, including wearing a hijab and predominantly working indoors, she began experiencing multiple painful and ulcerative scalp lesions that worsened over a year.
Three years prior to her latest diagnosis, the patient had her first concerning scalp lesion, which was later identified as trichoblastic carcinoma after surgical excision. As time elapsed, the emergence of additional nodular lesions ultimately led to a significant 6 x 9 cm excision on the right occipital scalp. Histopathological analyses revealed the presence of both trichoblastic carcinoma and verrucous carcinoma—two malignancies rarely associated with non-sun-exposed areas in EV patients.
The Implications of This Finding
This case challenges the established notion that UV exposure is a necessary component in the oncogenesis of SCC for EV patients. The researchers suggest that other factors, including genetic susceptibility or persistent viral infections, may play a significant role in the development of skin cancers in areas not typically exposed to sunlight.
Jebrini and colleagues, the authors of the study, emphasized the rarity and importance of this case, calling for enhanced monitoring and awareness in EV patients irrespective of their UV exposure history. This development compels dermatologists to reconsider their strategies for long-term patient management, especially concerning the use of systemic therapies that could aid in mitigating the risk of malignant transformations.
The Road Ahead: Unraveling New Risk Factors
As researchers continue to probe deeper, future studies may reveal additional risk factors that could contribute to the vulnerability of EV patients to skin cancers, even in shaded or protected regions of the body. Understanding these complexities could pave the way for new preventative measures and treatment paradigms, ensuring better outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.
In conclusion, this groundbreaking report serves not only as a reminder of the unpredictable nature of skin cancer but also as a clarion call for routine surveillance and vigilance among all patients with epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Stay informed as research unfolds in this critical area of dermatological health!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)