Shocking Anaphylactic Reaction to Tranexamic Acid in a Young Child: A Groundbreaking Case Study!
2024-09-30
Introduction
A recent case report has raised alarms in the medical community after a six-year-old girl from Iran experienced a severe anaphylactic reaction to tranexamic acid (TXA) during a routine surgical procedure. This child, with a medical history of unilateral cleft lip and palate, was admitted to Imam Hossein Children’s Hospital for elective surgery, marking another step in her ongoing treatment journey.
Medical History
At the time of admission, the girl weighed 20 kg and stood at 115 cm. She had undergone multiple surgeries to correct her cleft lip and palate, with the first operation occurring when she was just 20 days old. Despite her complicated medical history, which included congenital heart disease and hearing loss, her previous surgeries had been uneventful, leaving her family hopeful for a smooth recovery this time.
Anaphylactic Reaction
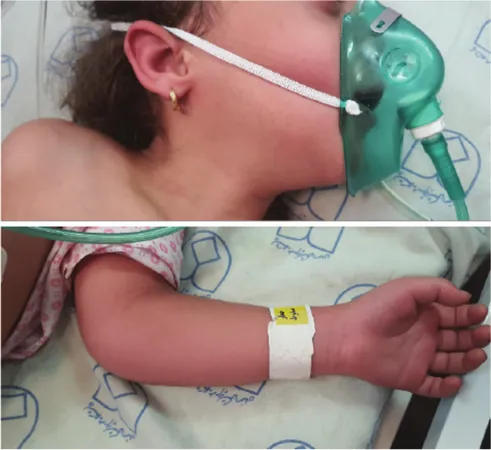
However, just one day after the surgery, things took a shocking turn. While the child had shown stable vital signs post-operation, the decision was made to administer TXA to control continued bloody secretions from her nasopharynx. Unfortunately, shortly after the infusion, she displayed alarming symptoms: respiratory distress, a significant drop in oxygen saturation, and widespread flushing across her body.
Immediate Response
Medical staff quickly suspected anaphylactic shock and sprang into action. Following pediatric advanced life support guidelines, they administered epinephrine and provided supplemental oxygen. Remarkably, after several doses of epinephrine, the child showed substantial improvement. Her blood pressure stabilized, and she regained consciousness, communicating with staff and family alike.
Potential Risks of TXA
This particular case sheds light on the often-overlooked risks associated with TXA, a commonly used medication during surgical procedures for both children and adults. While TXA is generally considered safe and effective in reducing blood loss without increasing thromboembolic risk, rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, have been documented in both adults and now children.
Monitoring and Diagnosis
The child was closely monitored for 24 hours following her anaphylactic Episode, and additional tests confirmed a possible IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to TXA. Medical professionals emphasize the difficulty in diagnosing anaphylactic reactions in children, as they may struggle to articulate their symptoms, leading to underreporting and misdiagnosis.
Conclusion & Recommendations
As the healthcare community grapples with the implications of this case, medical experts are reminded of the importance of thorough monitoring during and after TXA administration. This incident serves as a crucial reminder of the potential for severe allergic reactions, even to medications that are usually deemed low-risk. In a world where TXA is widely used, vigilance is key! Doctors are urged to maintain a heightened awareness for anaphylactic symptoms, ensuring timely intervention can make the difference between life and death.
Could this be a wake-up call for the medical community about the risks associated with seemingly innocuous medications? Only time will tell as clinicians strive to balance the benefits and potential risks of drug administration in pediatric populations.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)