Scientists Unlock the Secrets of Two-Photon Vision: A Revolution in Eye Care Awaits!
2024-11-04
Author: Wei Ling
Scientists Unlock the Secrets of Two-Photon Vision: A Revolution in Eye Care Awaits!
Scientists from the International Centre for Eye Research (ICTER) have made a groundbreaking advancement in the field of ophthalmic diagnostics by enhancing a technique known as two-photon vision. This innovative method holds tremendous potential for revolutionizing how we understand and treat various ocular conditions, paving the way for a brighter future in eye care.
Imagine being able to perceive an unseen spectrum of colors by looking through a kaleidoscope powered by invisible infrared light instead of simple lenses. This fascinating phenomenon relies on the interaction of pairs of photons—the fundamental particles of light—which allows the human eye to perceive pulses from infrared lasers, capturing the essence of the invisible world around us.
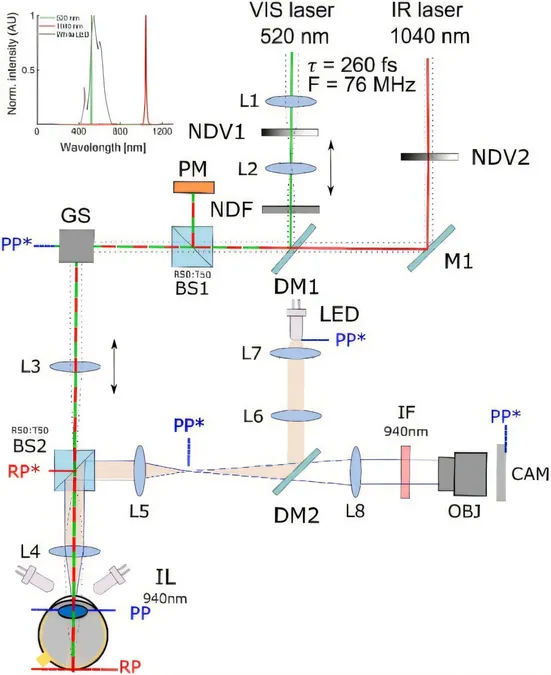
The key to harnessing this extraordinary vision lies in accurately measuring the brightness of these two-photon stimuli, a challenge that had previously stymied researchers. However, ICTER scientists have cracked the code and utilized photometric units to define the luminance of infrared light, establishing a new metric known as two-photon retinal illumination. This innovative approach lets us comprehend how these infrared stimuli can translate into perceivable light, unlocking new avenues in ocular research and treatment.
Two-Photon Vision Explained
The average human eye typically perceives electromagnetic waves ranging from approximately 380 nm to 780 nm—translating to visible colors from violet to red. However, many waves outside this spectrum, including infrared (wavelengths above 780 nm) and ultraviolet (below 380 nm), remain invisible without special devices. Surprisingly, the phenomenon of two-photon vision allows individuals to perceive these otherwise invisible infrared wavelengths by absorbing pairs of photons, leading to a perception of light that aligns with half the wavelength of the infrared source.
The scientists behind this research, including Ph.D. student Oliwia Kaczkoś, Ph.D. Eng. Katarzyna Komar, and Prof. Maciej Wojtkowski, demonstrated that the brightness of two-photon stimuli can reach impressive levels of nearly 670 cd/m², all while ensuring safe laser power for human eyes.
Applications Beyond Traditional Vision
The implications of two-photon vision extend far beyond academic curiosity. The technology has the potential to transform two major domains: medical diagnostics and cutting-edge experiences in virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR). Its unique properties allow for advanced diagnostic tests, particularly in neurology and ophthalmology, facilitating the monitoring of visual functions without relying on visible light that may cause discomfort or harm.
Imagine a future where eye care professionals can use this technology to assess eye health or neurological functions in a non-invasive and safe manner, utilizing infrared pulses for thorough examinations. Meanwhile, in the realm of VR/AR, creators can develop immersive visual experiences leveraging the unique characteristics of infrared light, amounting to richer interactions with digital worlds.
Innovative Research Fuels Future Developments
To confirm the viability and efficacy of two-photon stimuli, ICTER researchers proposed a novel methodology for expressing luminance in terms of standard photometric units. This new framework allows for the effective comparison of two-photon brightness with conventional single-photon vision displays, a significant advancement that could reshape how we build and perceive visual technologies.
With a focus on increasing the reliability and repeatability of measurements, the proposed system suggests that two-photon displays could soon become a key feature of advanced diagnostic tools, including innovative two-photon microperimetry and AR glasses.
As the research team presses on, the emergence of a new physical quantity—two-photon retinal illumination—set the stage for future explorations. The scientists' achievement marks a thrilling chapter in eye care, setting aside the limitations of traditional vision and opening doors for new diagnostic technologies and interactive experiences.
Stay tuned, as this research portends a wave of transformative developments in both medicine and technology, casting light on realms of vision previously thought to be forever shrouded in darkness!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)