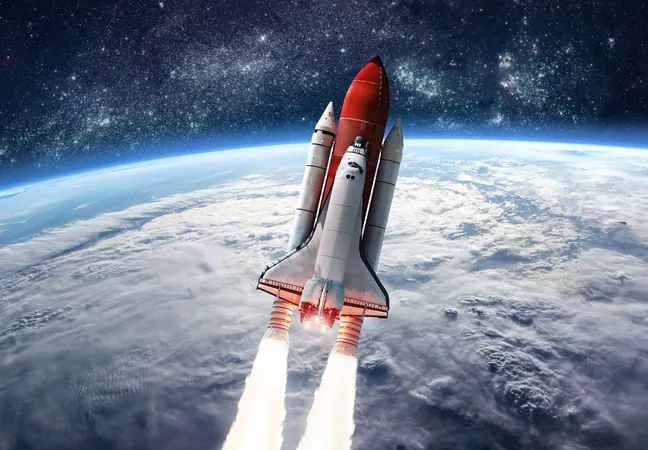

Rocket Launches: The Ozone Layer's Newest Adversary?
2025-07-21
Author: Ming
A Space Race to Save the Ozone Layer
The rapid surge in rocket launches could jeopardize Earth's ozone layer recovery, igniting concerns among researchers about the unforeseen environmental consequences of our burgeoning space industry.
Space Boom vs. Environmental Health
A collaborative study by scientists from the University of Canterbury and ETH Zurich reveals that pollution from rocket emissions and falling debris could significantly hinder the ozone layer's restoration.
Using sophisticated climate-chemistry models, the team analyzed how launches would impact ozone levels through 2030. Since 2019, we’ve seen the number of orbital launches explode from 97 to an anticipated 258 by 2024, with projections soaring beyond 2,000 annually by 2030.
Ozone Layer Under Siege
These emissions are particularly concerning as they persist much longer in the upper atmosphere compared to ground-level pollutants. Without natural cleansing mechanisms like rain, these toxins could circulate for years.
According to their model, if trends continue unchecked, the global ozone layer could face a thinning of nearly 0.3% by 2030, with seasonal losses over Antarctica potentially reaching alarming levels of up to 4%.
Why the Ozone Layer Matters More Than You Think
Though it might seem distant, the ozone layer is crucial to shielding life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can lead to skin cancer, cataracts, and more. It also plays a vital role in our ecosystems, especially in safeguarding marine life via phytoplankton health.
Even modest declines in ozone levels can amplify UV radiation reaching Earth, posing severe threats to both human health and the environment.
The Emission Dilemma
The core issue lies with emissions of chlorine gas and soot from rocket launches. Chlorine is known to deteriorate ozone molecules, while soot contributes to atmospheric heating, further fueling ozone-depleting reactions.
Currently, only rockets using cryogenic fuels like liquid oxygen and hydrogen are deemed nearly ozone-neutral, but these are used in just 6% of launches, leaving the majority contributing to this environmental crisis.
The Hidden Threat of Re-entry
While the study primarily concentrated on rocket ascent emissions, the return journey is equally problematic. As satellites re-enter the atmosphere, they release nitrogen oxides and metal particles, both of which pose significant risks to ozone integrity.
A Call to Action: Clean Fuels to the Rescue
"The alarming rise in rocket launches poses a risk to the vital ozone layer's recovery,' emphasizes researcher Sandro Vattioni. Yet, hope remains for mitigating this threat. Through better emissions monitoring, adopting cleaner fuels, and transitioning to cryogenic systems, we can protect our ozone layers.
Establishing international regulations could ensure the continued growth of the space industry aligns with the protection of our planet.
Conclusion: Time to Act Now!
As the race for space heats up, it is essential to prioritize the health of our ozone layer. Every effort to mitigate emissions can have a profound impact on our planet's future.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)