Rising Threat: Primary Cutaneous Infections by Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria — A Closer Look at 6 Disturbing Cases
2024-11-02
Author: Yu
Introduction
In recent years, the alarming increase in infections caused by non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) has prompted researchers to take a closer look at their cutaneous manifestations. This article highlights a study of six cases of primary cutaneous NTM infections, revealing critical insights into their clinical features, microbiological findings, and treatment outcomes.
The Rising Trend of NTM Infections
The incidence of NTM infections has surged, especially in dermatological presentations. These infections can stem from various sources, often related to trauma or immune suppression. The urgency for effective diagnosis and treatment is underscored by the often non-specific symptoms that mimic other dermatological conditions.
Study Overview
This retrospective study, conducted between June 2021 and June 2022 at Hangzhou Third People’s Hospital, focused on six patients diagnosed with primary cutaneous NTM infections. The analysis of clinical data and microbiological results from these cases sheds light on this worrying trend.
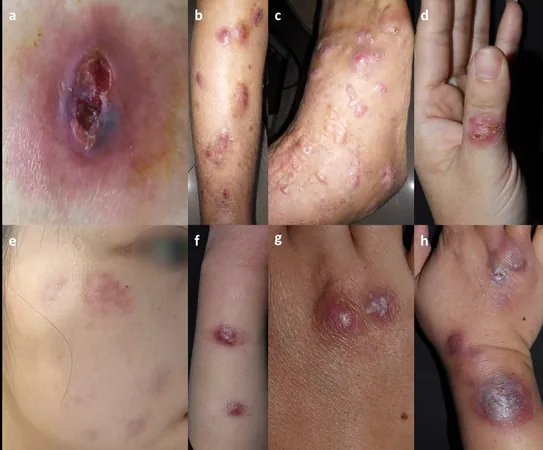
Findings: Uncovering the Cases
Among the six studied patients, four had prior trauma, while two had underlying conditions that compromised their immune systems. All presented with erythema nodular skin lesions, with varying locations on the body. Biopsies revealed granulomatous inflammatory changes consistent with NTM infections. Remarkably, laboratory cultures successfully identified four cases of Mycobacterium marinum, one Mycobacterium abscessus, and one Mycobacterium avium. Despite challenges with metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) in some cases, traditional cultures provided definitive results.
Profiles of the Affected Patients: A Closer Look
- **Case 1:** A 48-year-old woman with a painful abscess on her left hip, linked to her long-standing systemic lupus erythematosus. Notably, her lesions showed signs of infection after immunosuppressive therapy. - **Case 2:** A 64-year-old woman developed multiple erythematous nodules on her right leg post-ankle trauma, with no initial improvement from antifungals. - **Case 3:** A 39-year-old woman with an isolated thumb lesion presented blisters that evolved into erythema papules, indicating the unpredictable nature of these infections. - **Case 4:** A 27-year-old woman reported scattered plaques on her face after cosmetically invasive treatments, highlighting potential risks associated with cosmetic procedures. - **Case 5:** A 49-year-old female fisherman noted nodules on her left arm following fishing-related trauma, reinforcing the link between specific environments and NTM infection. - **Case 6:** A 37-year-old man had progressing lesions on his hand after regular fish tank cleaning, emphasizing the need for awareness of occupational hazards.
Conclusions: The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
The study emphasizes the often non-specific clinical features of primary cutaneous NTM infections and the challenges faced in accurately identifying the causative agents. The results suggest that in patients failing to respond to traditional treatment, a reassessment for atypical infections, particularly NTM, should be considered.
The Implications of NTM Infections
The rising incidence of NTM infections, particularly in the context of cutaneous disease, raises public health concerns. Understanding the associated risks, particularly for immunocompromised individuals or those who engage in activities exposing them to contaminated water or trauma, is vital. The advancements in diagnostic techniques, including the application of mNGS, show promise but also raise questions about their reliability and interpretation in clinical practice. The potential for mixed infections complicates the diagnosis, stressing the need for clinicians to employ a multifaceted approach when treating such complex cases.
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Against NTM
With the number of NTM infections on the rise, awareness and education are essential in both clinical settings and the public sphere. Prompt diagnosis and aggressive treatment, particularly in susceptible populations, can lead to favorable outcomes, as demonstrated by the majority of the cases studied. As we continue to monitor this growing trend, both medical professionals and patients must remain vigilant against these elusive pathogens. Stay informed and take precautions — you might just save yourself from a hidden danger lurking in your environment!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)