Revolutionizing Space Travel: Fusion Propulsion at the Forefront
2025-01-29
Author: Daniel
Introduction
In the quest for deeper space exploration, innovative propulsion systems have emerged as the key to unlocking our journey beyond Earth's confines. Traditional methods, such as chemical rockets, excel at escaping gravitational pulls but falter in the vastness of space. Electric propulsion offers long-term efficiency but lacks speed, while concepts like nuclear thermal rockets have yet to see the light of day in actual missions. Enter fusion propulsion—a pioneering technology that boasts both significant thrust and remarkable fuel efficiency, potentially transforming interplanetary travel and access to the solar system.
Helicity Space and the Heliophysics Mission
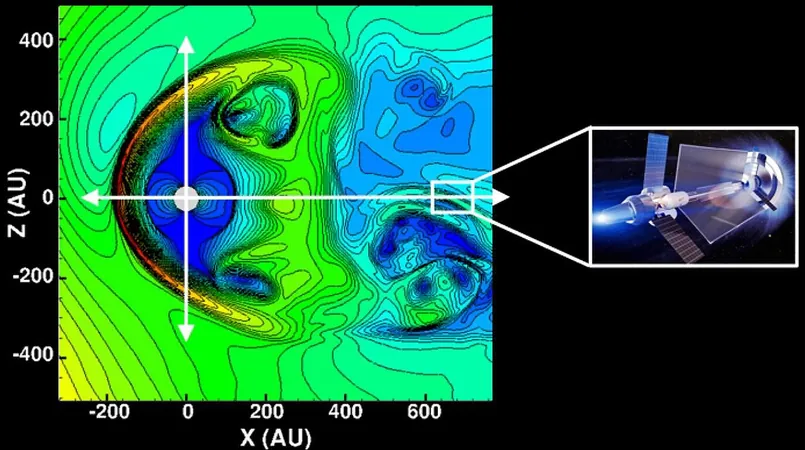
One ambitious company, Helicity Space, has recently garnered attention for its promising developments in fusion propulsion technology. Backed by a grant from NASA's Institute of Advanced Concepts (NIAC), Helicity is focused on exploring the heliosphere—the expansive region influenced by our Sun. This area, which includes the solar wind and cosmic rays, remains largely uncharted space due to the limitations of current spacecraft missions. Traditional probes like Voyager take decades to traverse the heliosphere's outer boundaries, leaving vast knowledge gaps in our understanding.
Helicity proposes a groundbreaking mission utilizing a network of fusion-powered spacecraft equipped with advanced sensors. These vessels will measure plasma characteristics, energetic particles, and even cosmic dust across different regions of the heliosphere, promising to provide invaluable data that heliophysicists have long sought.
Challenges and Advances in Fusion Propulsion
But the real excitement behind Helicity’s NIAC grant doesn't solely rest on the sensors; it revolves around revolutionizing propulsion technology. While many have dreamed of fusion propulsion for decades, achieving a practical application has remained elusive, hampered by the complexities of plasma containment and fusion processes. Projects like the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) exemplify this struggle, often requiring exorbitant budgets and extensive timeframes—ITER is not expected to reach operational capacity until 2035.
In contrast, Helicity, a dynamic start-up based in Pasadena, aims to develop a functional fusion engine far earlier than its larger counterparts. Co-founder and chief technologist Setthivoine You explains that unlike fusion power plants, which need to deliver consistent, high energy outputs for financial viability, their engine only needs to achieve a tenfold energy gain occasionally, significantly simplifying the engineering challenges.
The Future of Space Travel
Helicity's prototype is already making waves, showcased at various conferences and in academic publications. The NIAC funding enables the team to refine the fusion engine's design to meet the unique requirements of their heliosphere exploration mission. Notably, the technology also holds the promise of drastically reducing travel time to Mars to just six weeks, compared to the conventional nine-month journey.
Even more audacious are ideas for missions utilizing the solar gravitational lens effect to directly image distant exoplanets. Dr. You anticipates that their fusion engine could facilitate such journeys in under a decade—far quicker than existing proposals that rely on solar sails or other traditional propulsion methods.
Broader Applications and Challenges Ahead
Beyond its futuristic propulsion system, Helicity is also committed to advancing technologies with earthly applications. This could include developments in high-efficiency energy storage solutions, state-of-the-art magnetic coils, and advanced solid-state switches.
Despite the complexities that lie ahead—especially in refining the systems involved in plasma generation and maintaining operational functionality in space—Helicity Space is well-positioned for success. The start-up enjoys backing from influential venture capital firms and major aerospace players like Airbus and Lockheed Martin. With a working prototype already in hand, Helicity's ambitious goal to integrate fusion power for space travel could soon pivot from a dream to an ambitious reality.
Conclusion
As we stand on the brink of a new era in space exploration, the successful realization of fusion propulsion could not only redefine our exploratory capabilities but also pave the way for humanity's long-awaited expansion throughout the solar system. Are we ready to embrace this revolutionary leap into the cosmos?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)