Revolutionizing Space: Prosthetic Mobility Tested in Zero Gravity
2025-05-28
Author: Mei
A Groundbreaking Step in Space Medicine
In a monumental breakthrough for space exploration, a lower limb prosthesis has been rigorously tested in microgravity during the European Space Agency's (ESA) latest flight campaign aboard the renowned 'Zero G' aircraft.
Meet the Astronaut Trailblazer: John McFall
ESA astronaut reserve John McFall, a courageous through-knee amputee, took center stage as he navigated a series of demanding activities—squatting, walking, and running—across more than 90 parabolas during three exhilarating flights. Each maneuver created 22-second microgravity intervals, mimicking the conditions encountered aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
An Innovative Initiative: ESA's Fly!
Kicking off on May 21, 2025, from Bordeaux, France, these groundbreaking test flights were part of ESA's 86th parabolic campaign. McFall served as an invaluable subject matter expert in ESA's Fly! initiative, aimed at breaking down the barriers preventing lower limb amputees from taking part in extended space missions.
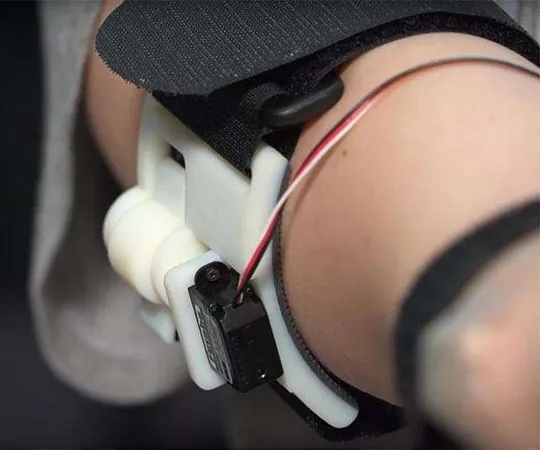
The Cutting-Edge Prosthesis: Ampu-T2
McFall's prosthetic leg is a marvel of technology, featuring a mechatronic 'smart' knee and interchangeable components designed for everything from daily living to athletic performance. This advanced prosthesis is equipped with sensors that typically rely on gravity, prompting the Fly! research team to create the Ampu-T2 experiment to test its functionality in a weightless environment.
Collaborative Research for Groundbreaking Data
Collaborating with orthopedic technology leader Ottobock, researchers meticulously gathered performance data. Initial trials began with basic activities such as standing and walking, leading to more complex tasks like running, all while adjusting blade stiffness and knee resistance. To simulate the necessary load forces in microgravity, a harness and elastic cords were used, mirroring the exercise gear used on the ISS.
Impacts Beyond the Stars
The insights gleaned from these tests will be pivotal in determining the most effective setup for prosthetics in daily life aboard the ISS. But this research extends further than technological advancements. On Earth, maintaining bone density through regular walking is crucial, but astronauts suffer rapid bone and muscle loss in space. Current ISS exercise regimens—comprising treadmills, bicycles, and resistance devices—aim to counteract this issue. McFall's pioneering tests could pave the way for tailored training protocols for prosthetic users in orbit, ensuring that all astronauts maintain their health during missions and upon their return to Earth.
Towards an Inclusive Space Future
The Fly! initiative stands as a testament to ESA's dedication to advancing inclusivity in space exploration and preparing for the diverse crews of the future. With each leap forward, the possibilities for a truly inclusive journey into space are becoming more tangible.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)