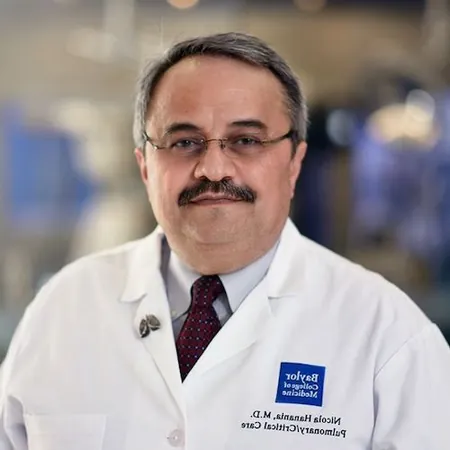

Revolutionizing Severe Asthma Treatment: The Rise of Biologics and Biomarkers
2025-07-11
Author: Daniel
Transforming Asthma Care Over the Last Decade
In the past ten years, the landscape of severe asthma treatment has undergone a monumental shift. With the introduction of targeted biologic therapies like omalizumab, mepolizumab, benralizumab, dupilumab, and the newly approved tezepelumab in 2021—marked as the first biologic to treat severe asthma irrespective of baseline eosinophil levels—patients now have an unprecedented range of options. These advancements are setting a fresh benchmark for the treatment of type 2-high asthma, emphasizing the role of biomarkers in determining eligibility for these innovative therapies.
A New Era of Personalized Medicine
As these therapies become available, the expectations for achieving better disease control and enhancing long-term outcomes are rising. The focus on early diagnosis and tailored therapy selection, underpinned by continuous biomarker assessment, is redefining asthma management. While clinicians now face a bewildering array of therapeutic choices and intricate eligibility criteria, the hope for reduced reliance on steroids, fewer exacerbations, and improved quality of life is promising.
Insights from Leading Pulmonologists
At a recent clinical forum hosted by HCPLive in Houston, Texas, a cadre of pulmonologists, spearheaded by Dr. Nicola A. Hanania of Baylor College of Medicine, delved into the practicalities of integrating these advancements into everyday practice. They explored the importance of sequencing biologics, understanding the implications of biomarkers such as eosinophils and FeNO, and emphasized the need for a structured early referral process.
Steroid Compliance: An Ongoing Challenge
One panelist notably pointed out that despite the advancements, proper use of steroid inhalers remains critical. "Compliance with steroid inhalers is still our biggest challenge; patients often relapse once they feel better and discontinue use," they stated.
Navigating Real-World Challenges
The panel highlighted how type 2 inflammation remains a focal point in asthma treatment, with eosinophils, FeNO, and IgE levels guiding therapy decisions, although real-world challenges—such as access to treatments, patient education, and insurance issues—still persist. The discussion made it clear that optimizing biologic therapies in practical settings is now essential for realizing their full potential.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Collaboration
Dr. Hanania reiterated the importance of collaboration with primary care providers to identify and manage high-risk patients effectively. "Not every asthma case requires intensive phenotyping, but specialists need to focus on the more complex cases," he explained.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Biologics
As the group wrapped up their discussion, they reflected on the long-term efficacy of biologics in asthma treatment. While robust real-world evidence underpins their effectiveness, uncertainties around treatment tapering and ongoing monitoring of biomarkers remain. The conversation also turned toward the future, contemplating emerging needs in COPD management and the potential for dual-target or multi-mechanism therapies that could further transform asthma care.
Call for Broader Experimentation
One panel member encapsulated the sentiment perfectly, stating, "Each biologic deserves thorough exploration. We must enhance accessibility and utilization of these innovative treatments for all patients."




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)