Revolutionizing Reproductive Health: How Mobiluncus mulieris is Unraveling the Secrets of Adverse Outcomes
2025-08-08
Author: Arjun
The Crucial Role of Vaginal Microbiota in Reproductive Health
Imagine a world where the delicate balance of the vaginal microbiota dictates reproductive health! Recent studies reveal that the vaginal microbiome significantly impacts reproductive outcomes by interacting with epithelial barriers and shaping local immune responses. Disruptions in this balance, like a depletion of beneficial Lactobacillus species, are often linked to bacterial vaginosis (BV) and a host of reproductive issues including preterm births and infertility. This brings us to the spotlight: Mobiluncus mulieris.
Mobiluncus mulieris: The Hidden Threat
While often overshadowed by more notorious bacteria, Mobiluncus mulieris holds significant sway in the realm of reproductive health. Found rarely in healthy women, this gram-positive bacterium can activate immune receptors, triggering inflammatory responses that may lead to dire reproductive outcomes.
Unveiling Epithelial Interactions
The complexities of host-microbe interactions in the lower reproductive tract reveal just how specialized these interactions can be. Different types of epithelial cells exist: vaginal cells, which lack tight junctions, and cervical cells, which produce mucus. This study dives into how M. mulieris may interact uniquely with each type, potentially steering reproductive health in alarming directions.
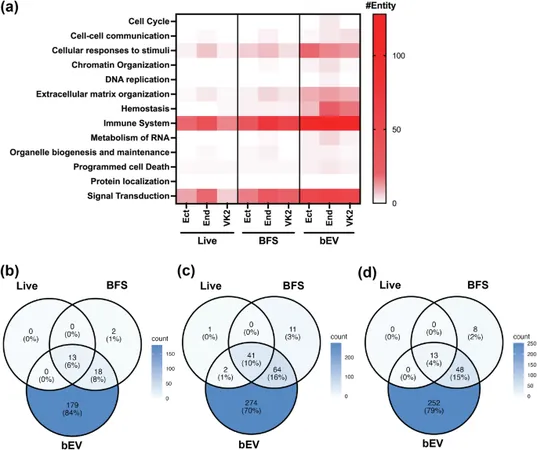
Decoding the Transcriptional Impact
By employing cutting-edge RNA sequencing, researchers have uncovered that exposure to M. mulieris, including its bacterial-free supernatant and extracellular vesicles, dramatically alters gene expression in cervicovaginal epithelial cells. Specifically, the presence of extracellular vesicles amplifies immune system-related changes, suggesting a unique role in shaping inflammatory responses.
Transcriptional Effects: A Call to Action
Notably, gene expression analyses demonstrate that M. mulieris not only affects inflammatory pathways but also disrupts vital cellular functions. This disruption can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, including STIs, illustrating the urgent need for deeper understanding and potential therapeutic interventions.
A TLR2-Driven Inflammatory Response: What It Means
The study emphatically shows that the immune response triggered by M. mulieris largely hinges on TLR2 activation. This discovery opens up new avenues for targeted treatments that could mitigate the inflammation linked to this sneaky pathogen and protect reproductive health.
Real-Life Implications: Tying It All Together
In clinical comparisons, women with elevated M. mulieris showed higher levels of MMP9, a marker associated with preterm labor. This correlation reminds us of the broader implications of maintaining a healthy vaginal microbiota, emphasizing the need for continuous research and the potential development of new treatment strategies that address M. mulieris-induced reproductive risks.
The Path Forward: Keep an Eye on M. mulieris
This groundbreaking research encourages us to keep a vigilant eye on M. mulieris and its role in reproductive health. By deciphering the complexities of this microorganism's interactions and effects, we can strive for better clinical outcomes and improved reproductive health strategies worldwide.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)