Revolutionizing Musculoskeletal Medicine: The Power of Spatial Transcriptomics
2025-06-09
Author: Nur
A Breakthrough in Understanding Bone and Muscle Health
In the world of biology, understanding gene expression has come a long way, yet one critical element has often been overlooked: the spatial context. Traditional methods like bulk RNA sequencing and single-cell RNA sequencing provide valuable insights, but they fall short by not revealing how cells interact or how gene activity varies within the intricate architecture of tissues. This lack of spatial information can impede our efforts to fully grasp developmental processes, injuries, and diseases affecting the musculoskeletal system.
Unveiling Insights Through Spatial Transcriptomics
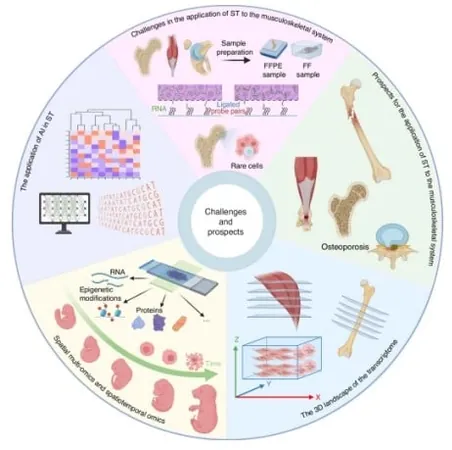
A groundbreaking review published in *Bone Research* in May 2025 by researchers from Hebei Medical University, Xiamen University, and Huazhong University of Science and Technology highlights the transformative potential of spatial transcriptomics (ST). This innovative approach offers an in-depth analysis of gene expression, enhancing our understanding of conditions such as arthritis and muscle degeneration. The research team meticulously catalogs recent advancements in ST technologies, showcasing how these tools are utilized to elucidate developmental pathways and disease mechanisms.
Comparing Technologies: Imaging vs. Sequencing
The review dives into two primary classes of spatial transcriptomics: imaging-based and sequencing-based techniques. Imaging methods like RNAscope and the cutting-edge multiplexed error-robust fluorescence in situ hybridization (MERFISH) allow for precise detection of specific genes, whereas sequencing-based technologies like Visium and Stereo-seq provide widespread transcriptome views across larger tissue regions.
Unlocking the Secrets of Development and Disease
Utilizing these powerful tools, researchers have made significant strides in unpacking complex processes such as human limb development, identifying stem cell niches, and elucidating gene expression patterns in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and tendon injuries. Notably, spatial transcriptomics has allowed scientists to map the cellular layout of the intervertebral disc, pinpointing progenitor cells essential for tissue regeneration. In another fascinating case, it revealed how scar-forming macrophages inhibit muscle repair after an injury.
A Roadmap for Future Research
The review also serves as a vital guide for researchers venturing into the dynamic field of spatial transcriptomics. It outlines a step-by-step approach for selecting the right ST platforms based on various factors such as resolution, budget, species specificity, and research goals.
A Vision for the Future of Musculoskeletal Medicine
According to Prof. Wei Chen, a prominent orthopedic surgeon and co-author of the review, spatial transcriptomics fundamentally enhances our understanding of musculoskeletal biology. It shines a spotlight on where genes are active in intact tissues, intertwining gene functions with spatial organization. This cutting-edge technology is anticipated to become a cornerstone in orthopedic and regenerative medicine, paving the way for new disease therapies and innovative treatment strategies.
As spatial transcriptomics continues to evolve, its implications for personalized medicine are profound. Emerging advancements in 3D spatial mapping, spatial multi-omics, and artificial intelligence promise to amplify the capabilities of ST, heralding a new era in musculoskeletal care. The future looks bright, with potential developments in personalized therapies, advanced biomaterials for tissue repair, and targeted drug delivery, firmly positioning spatial transcriptomics at the core of next-generation musculoskeletal medicine.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)