Revolutionizing Mental Health Diagnostics: How AI is Unlocking the Power of Niacin Skin-Flushing
2025-08-04
Author: Daniel
Introduction: A Game Changer for Psychiatric Disorders
Imagine having a tool that could revolutionize the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders, from depression to schizophrenia, using just a simple physiological response. Enter the Niacin Skin-Flushing Response (NSR), a groundbreaking biomarker that researchers are utilizing to enhance diagnostic accuracy in mental health.
Harnessing AI: The Future is Here
Traditional diagnostic methods for mental illnesses can be convoluted and time-intensive, leaving many in limbo. However, a recent study has unveiled a cutting-edge approach that combines an open-access dataset with artificial intelligence (AI) technology to redefine how we understand and diagnose psychiatric conditions. By leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms, this research intends to make NSR analysis a standard practice in psychiatric diagnostics.
The Novel Dataset: A First in the Field
This study introduces the world’s first open dataset dedicated to studying NSR in relation to psychiatric disorders. With 600 high-quality images sourced from 120 individuals—including both healthy controls and patients across various psychiatric conditions—the dataset aims to set a new benchmark for research in the field. Unlike previous studies limited to specific disorders or requiring specialized devices, this open-access collection supports a broader application of machine learning techniques.
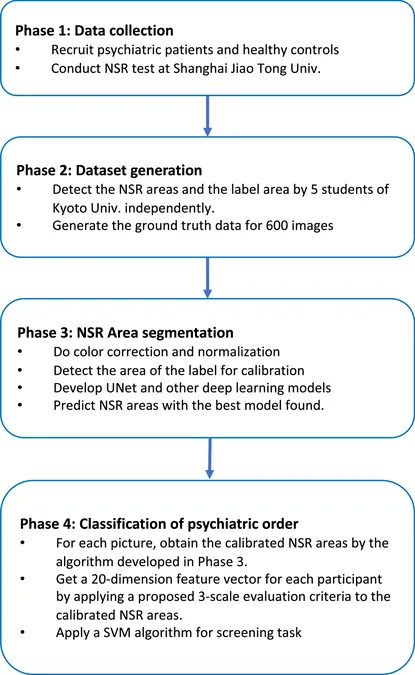
How It Works: From Segmentation to Classification
At the heart of this innovative approach is a sophisticated method that employs an Efficient-Unet based deep learning model for precise segmentation of NSR areas. This is further enhanced by rigorous data augmentation techniques and robust training protocols, allowing for improved accuracy in detecting skin flushing responses.
To classify psychiatric disorders, researchers utilized a Support Vector Machine (SVM) which analyzes feature vectors drawn from the segmented NSR areas. This dual-step process not only ensures a thorough analysis but also accommodates diverse conditions without dependency on specific devices.
Impressive Results: Accuracy Meets Objectivity
The AI-driven diagnostic method has shown remarkable results, achieving a sensitivity between 60% to 65% and specificity ranging from 75% to 88%. This suggests a broad applicability capable of delivering quick and precise diagnostics across various mental health disorders, further stressing the relevance of NSR in aiding clinical assessments.
Conclusion: A New Dawn for Mental Health Diagnostics
In summary, this pioneering research highlights the transformative potential of utilizing advanced AI tools in psychiatric diagnostics, demonstrating that machine learning could indeed surpass human capability in terms of speed and accuracy. With the availability of this unique, device-independent dataset, the study not only establishes a new frontier in mental health evaluation but also opens the door for future innovations.
As we continue to explore the capacity of NSR and AI, we look forward to a future where mental health diagnostics are not only more accurate but also more accessible, paving the way for better outcomes and improved lives across the globe.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)