Revolutionizing Hydrogen Production: New Findings on Bubble Behavior Could Boost Efficiency
2025-09-22
Author: Siti
A Breakthrough in Green Hydrogen Production
In a groundbreaking study led by David Fernandez Rivas at the University of Twente (UT), researchers have unveiled vital insights into bubble dynamics during hydrogen production. This research, featured in a special collection celebrating the Global Young Academy's (GYA) 15th anniversary, highlights a novel approach to optimizing the electrolysis process for the production of green hydrogen.
Celebrating Young Scientists
The GYA, co-founded by UT professors Hans Hilgenkamp and Wilfred van der Wiel in 2010, has blossomed into a pivotal platform for emerging researchers globally. As it celebrates 15 years of promoting scientific innovation, it invited contributions to showcase how young scientists tackle challenging global issues.
Controlling Bubbles for Better Efficiency
Hydrogen production typically involves splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen via electrolysis, a process often hindered by random bubble formation on electrode surfaces. These uncontrolled bubbles can obstruct efficiency, prompting the UT team to seek a solution.
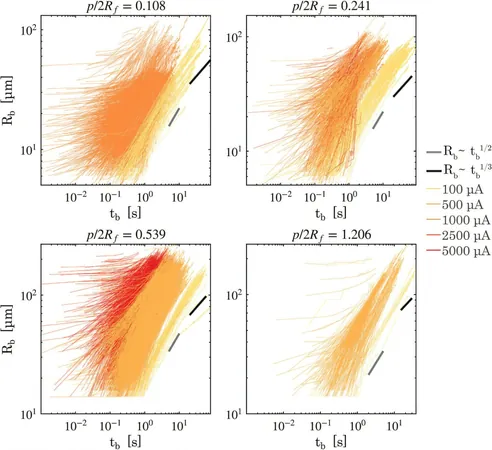
Utilizing resources from the Nanolab cleanroom at the MESA+ Institute, the researchers designed silicon electrodes featuring strategically placed hydrophobic cavities. These tiny pockets facilitate consistent bubble formation, drastically reducing randomness and enhancing the controllability of the electrochemical process.
The Impact of Bubble Spacing
One of the standout aspects of this study was the team's manipulation of the spacing between these cavities. By adjusting the distance, they observed varying behaviors in how bubbles grew, merged, and detached based on their proximity to neighboring cavities.
The results were fascinating: closer cavities led to more frequent breaking off of bubbles in smaller sizes. This not only diminished gas accumulation but also increased bubble coverage on the electrode surface. While this discovery introduces a trade-off that requires careful consideration, it opens up new avenues for optimizing hydrogen production efficiency.
Published Insights in Scientific Community
This innovative work is documented in the journal Small, marking a significant step towards enhancing the viability of green hydrogen as a sustainable energy source. With these findings, the research team aims to pave the way for future advancements in electrolysis technology.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)