
Revolutionizing Home Robotics: New AI Dataset Connects Language to 3D Spaces
2025-06-16
Author: Jia
A Game-Changer for Embodied AI
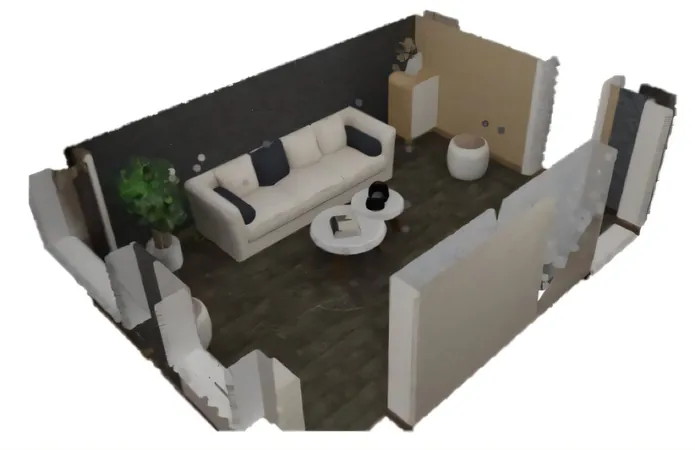
In a groundbreaking advance that could redefine household robotics, researchers from the University of Michigan have unveiled a revolutionary dataset dubbed 3D-GRAND. This extensive and intricately annotated 3D-text dataset enables embodied AI—like robots in our homes—to effectively link language with our three-dimensional world. This innovative study was spotlighted at the prestigious CVPR Conference in Nashville, Tennessee, on June 15 and made available on the arXiv preprint server.
Surpassing Expectations with Groundbreaking Accuracy
When rigorously tested, the AI model trained on 3D-GRAND achieved an astonishing 38% grounding accuracy, surpassing the previous benchmark by a remarkable 7.7%. Even more impressive, the rate of AI-generated 'hallucinations'—incorrect outputs—plummeted to just 6.67%, down from a troubling 48%.
Next-Gen Robots: More Than Just Vacuums
Imagine a future where you can command your robot to fetch specific items, like "pick up the book next to the lamp on the nightstand and bring it to me." To bring this vision to life, robots must first comprehend what our language signifies in a spatial context. Joyce Chai, a leading professor of computer science at U-M, emphasized, "If we want a robot to interact with us, it must fully grasp spatial terms and object orientations in a rich 3D environment."
The Challenge and Triumph of 3D Data
Despite the wealth of information accessible through text and image-based AI, 3D data remains significantly scarce, especially data that connects specific words to their corresponding 3D objects. Traditionally, curating such data requires immense time and manpower, but this research team took a different route.
Harnessing Generative AI for Synthetic 3D Rooms
By leveraging generative AI, the researchers produced synthetic rooms, automatically annotating the 3D structures within them. The resulting 3D-GRAND dataset boasts an impressive 40,087 household scenes combined with 6.2 million rich, grounded descriptions.
Cutting Costs and Time Drastically
Jianing Jed Yang, the study's lead author and a doctoral student, highlighted the efficiency of synthetic data: "The labels come for free because you already know where every object is located, simplifying the curation process immensely." After generating the 3D data, advanced AI models meticulously described attributes like color and shape, ensuring precise connections between language and 3D objects.
Human Quality Control Ensures Reliability
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the dataset, human evaluators spot-checked over 10,200 room-annotation pairs, yielding an error rate comparable to human annotations at a mere 5% to 8%.
A Leap Forward in AI Model Development
The capacity to produce 6.2 million high-quality annotations in just two days marks a significant leap forward in crafting effective AI models, as Yang noted. The research team trained a model using 3D-GRAND and validated its performance against established baseline models. The new benchmark demonstrated a substantial increase in grounding accuracy while drastically reducing hallucination rates.
Looking Ahead: Robots that Truly Understand Space
With the introduction of 3D-GRAND, the research team is poised to explore the next frontier—testing on actual robots. "It will be thrilling to see how 3D-GRAND empowers robots to better navigate and comprehend space, ultimately enhancing their interaction and collaboration with humans," stated Chai, as the future of home robotics inches ever closer.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)