Revolutionizing Heart Failure: Unveiling the Secrets of Cardiometabolic HFpEF
2025-07-03
Author: Yu
Understanding HFpEF: The Silent Epidemic
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a rising concern in cardiovascular health. Characterized by breathlessness even with minimal exertion, this condition affects millions and presents a staggering 40% mortality rate over five years, highlighting its reputation as the ‘largest unmet need in cardiovascular medicine.’
A Surge in Cardiometabolic Disorders
But what’s driving the surge? The answer lies in the global epidemic of cardiometabolic diseases linked to modern lifestyles, where diabetes and obesity rates are skyrocketing. By 2045, it’s predicted that diabetes cases will increase by a shocking 46%, impacting nearly 650 million individuals. As obesity closely correlates with heart disease, the obesity epidemic can be seen as a direct catalyst for the rising incidence of HFpEF.
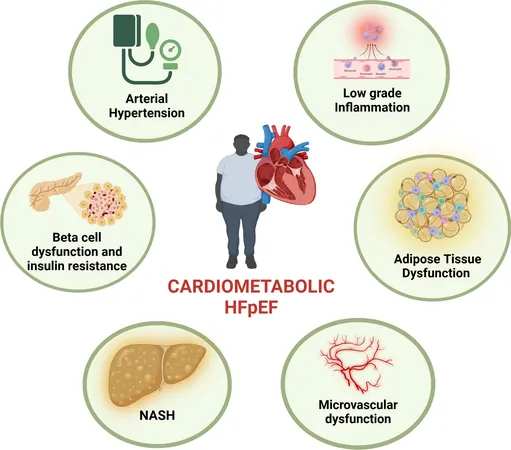
Revealing the Cardiometabolic Phenotype
Distinctly intertwined, obese patients develop a unique heart failure phenotype known as cardiometabolic HFpEF. In this group, weight management strategies such as dietary restrictions and new treatments like GLP-1 receptor agonists (e.g., semaglutide) have shown incredible promise. The STEP HFpEF trial recorded significant weight loss and improvements in exercise function among participants.
The Role of Visceral Adipose Tissue
Emerging data reveals that fat buildup, particularly around the heart, significantly affects heart health. Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) is a double-edged sword—it provides energy to the heart but, under stress from obesity, transforms into a source of inflammation, fueling further cardiac dysfunction. This highlights the urgent need for innovative approaches to tackle the challenges posed by visceral fat.
Molecular Mechanisms: The Hidden Culprits
Complex metabolic and immune pathways converge in HFpEF, creating a storm of cardiac inflammation and dysfunction. The interplay between insulin resistance and chronic inflammation leads to increased oxidative stress, driving heart injury and dysfunction. Understanding these molecular mechanisms is crucial for developing new treatment avenues.
Innovative Treatment Frontiers
Despite the growing understanding of HFpEF, effective treatments remain elusive, with traditional therapies failing to meet primary efficacy outcomes. However, groundbreaking studies showcase the positive impacts of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists, now recognized as guideline-recommended treatments for HFpEF. Yet, the challenge remains: while these drugs improve symptoms, their effects on mortality are modest.
The Future of Personalized Medicine
As HFpEF is set to become the most prevalent type of heart failure in the coming years, the need for personalized treatment is more pressing than ever. Advancements in epigenetics and molecular research may pave the way for therapies tailored to individual profiles, opening doors to more effective and specific interventions.
The Importance of Lifestyle Changes
Beyond pharmacological treatments, lifestyle modifications like weight loss, calorie control, and physical exercise play a pivotal role in managing HFpEF. Diets, stress management, and sleep optimization can dramatically influence health outcomes, shining a light on the importance of holistic approaches to treatment.
Conclusion: A New Era in HFpEF Management
Though managing cardiometabolic HFpEF presents significant challenges, the combination of advanced pharmacology and personalized medicine offers new hope. As studies continue to unravel the complexities of this condition, clearer pathways for innovative treatments are emerging, pointing to a promising future in the battle against heart failure.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)