Revolutionizing Food Safety: PET Plastics Get an Antimicrobial Upgrade with Plasma and Zinc Nanoparticles
2025-08-21
Author: Wei Ling
The Importance of Polymers in Food Packaging
Polymers play a pivotal role in modern food packaging, prized for their cost-effectiveness, lightweight nature, flexibility, and chemical stability. They serve as vital barriers, shielding food from moisture, oxygen, sunlight, and harmful microorganisms that can cause spoilage and health risks. Among these materials, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) stands out for its transparency, durability, and exceptional mechanical properties.
Overcoming Challenges with Conventional PET
Despite its advantages, conventional PET and similar low-cost polymers face challenges in surface characteristics such as wettability, adhesion, and microbial resistance. However, a fascinating new approach harnesses cold plasma treatment combined with zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO) to significantly enhance the antimicrobial properties of PET.
Breakthrough Research from Zagreb
A pioneering team of scientists from the Institute of Physics in Zagreb, collaborating with various partners, has unveiled a groundbreaking method to create PET/ZnO composites from conventional PET foils. This innovative research was recently published in 'Applied Surface Science Advances'.
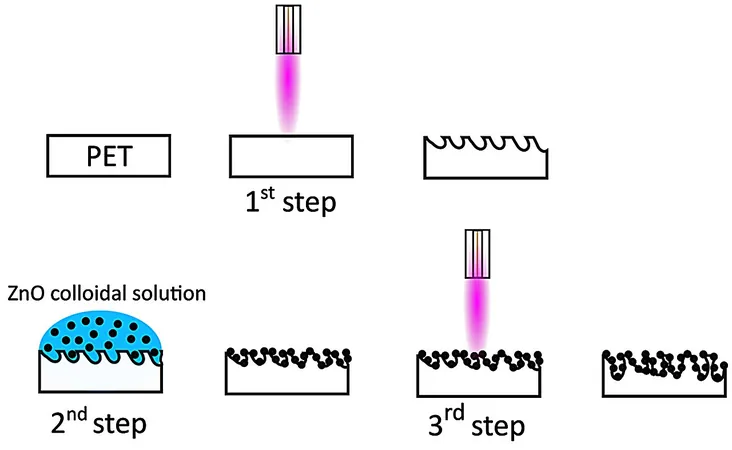
Innovative Processes Yield Enhanced Properties
The process involves an atmospheric pressure plasma jet (APPJ) to treat the PET foils, followed by coating them with ZnO nanoparticles. Repeating the plasma treatment embeds these particles securely into the surface, forming a unique two-dimensional incorporation that significantly boosts PET's antimicrobial activity.
Cutting-Edge Techniques for Nanoparticle Production
To synthesize the ZnO nanoparticles, the researchers utilized pulsed laser ablation in water, ensuring top-notch purity. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) studies demonstrated that the plasma treatment roughened the PET surface, increasing its texture from 6 nm to 13 nm and distributing nanoparticles evenly.
Safety and Effectiveness Confirmed
Importantly, leaching tests confirmed that nearly all Zn particles remained securely embedded in the PET surface, ensuring performance, environmental safety, and sustainability. The enhanced PET materials exhibited an impressive 29% increase in UV protection, preserving food quality over extended periods.
Reinforced Material with Remarkable Antibacterial Properties
While the plasma treatment did decrease PET's elasticity, the addition of ZnO nanoparticles, specifically between 200–500 µL, reinforced the material. Most astonishingly, at the highest tested ZnO concentration (245.75 mg Zn/kg PET), the composites achieved nearly 100% antibacterial efficiency against notorious pathogens like Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
A New Era for Food Packaging?
This revolutionary development in PET technology not only enhances food safety but also offers sustainable solutions to environmental challenges. As the fight against foodborne illnesses continues, the integration of antimicrobial properties into food packaging through innovative techniques like these could reshape the future of food preservation.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)