Revolutionizing Detection of Swimmer's Itch: New Molecular Toolkit Unveiled
2025-05-30
Author: John Tan
The Swimmer's Itch Epidemic: A Growing Concern
Cercarial dermatitis, commonly referred to as swimmer's itch, is a waterborne skin condition triggered by the invasion of larval schistosomes (cercariae) from birds. With rising incidences around the globe, swimmer's itch is increasingly recognized as a (re)emerging threat, affecting not only public health but also local economies, especially in recreational waters.
The Challenge: Outdated Detection Methods
Traditional detection methods, like cercarial shedding assessments and snail dissections, are not only laborious but also fall short in sensitivity. As outbreaks escalate, the urgency to implement more effective monitoring techniques becomes critical.
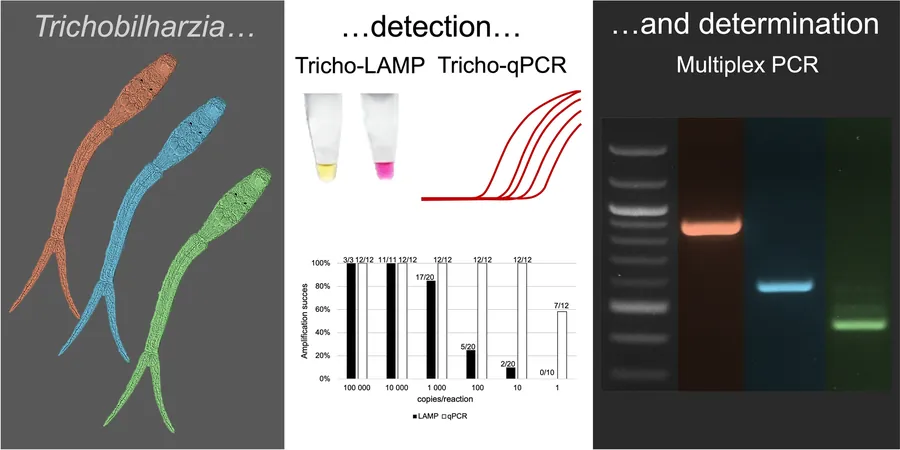
Introducing a Game-Changing Solution: A Molecular Toolkit
In response to these challenges, a groundbreaking molecular toolkit has been developed, integrating Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP), quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR), and multiplex PCR. This trio of techniques promises rapid, sensitive, and reliable identification of Trichobilharzia species from various biological samples.
Breaking Down the Methodology
The toolkit features Tricho-LAMP and Tricho-qPCR, fine-tuned for precise Trichobilharzia DNA detection. The multiplex PCR enhances species identification, specifically targeting three prevalent European species: Trichobilharzia franki, T. szidati, and T. regenti.
Impressive Results: Sensitivity that Matters
Tricho-LAMP has shown remarkable sensitivity, detecting T. regenti and T. franki at concentrations as low as 10⁻³ ng, while T. szidati can be identified at 10⁻² ng per reaction. Further tests with synthetic DNA indicated effective amplification at varied concentrations. On the other hand, Tricho-qPCR demonstrated outstanding sensitivity, reaching detection limits of 10⁻⁴ ng and single copy identification with impressive accuracy.
Conclusions: A New Era of Monitoring
This innovative toolkit offers comprehensive capabilities for environmental monitoring, empowering researchers and public health authorities. With Tricho-LAMP and Tricho-qPCR ready to tackle environmental DNA (eDNA) challenges and multiplex PCR facilitating straightforward species identification, the future of swimmer's itch control looks promising.
Why It Matters: The Broader Impact
These advanced detection methods not only enhance our understanding of Trichobilharzia but also lay the groundwork for timely outbreak responses. As cases increase, this toolkit's ability to deliver rapid results could be pivotal in preserving public health and safeguarding water-related recreational activities.
From the Lab to the Field: Practical Applications
While LAMP excels in rapid detection, the qPCR method offers precise quantification for deeper insights. The multiplex PCR allows for quick identification without the need for sequencing—a crucial advantage as differentiating between species can often be complicated.
Final Thoughts: Combating Swimmer's Itch Effectively
As swimmer's itch continues to pose challenges across Europe and beyond, the introduction of this molecular detection toolkit represents a significant leap forward in effective monitoring and management strategies. The integration of these molecular techniques stands to revolutionize our approach to tackling this vexing issue.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)