Revolutionizing Desalination: How Wet Membrane Structures Can Transform Water Purification
2025-08-25
Author: Sarah
Breakthrough Study Unveils Membrane Mysteries
A groundbreaking study from a collaboration between researchers at the Technion Israel Institute of Technology and the University of Texas at Austin is shaking the foundations of desalination technology. Featured as the cover article in ACS Nano, this research could spell a revolution in how we understand and utilize membranes for water purification.
Wet vs. Dry Membranes: A Game Changer
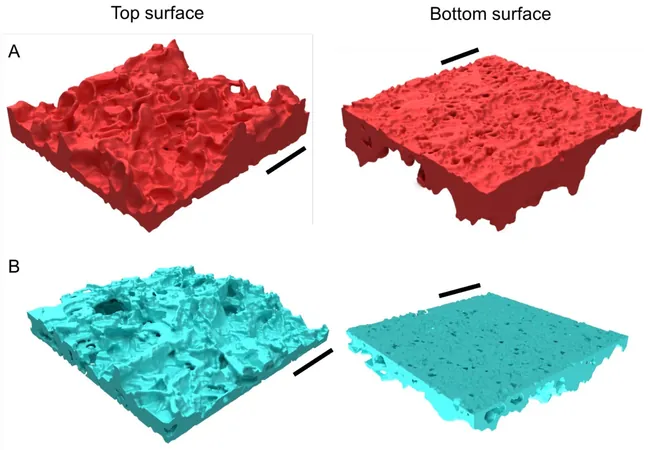
Unlike prior studies that focused solely on dry membranes, this innovative research examined how membranes perform when they are saturated with water. The findings revealed striking differences that could significantly enhance membrane efficiency in desalination processes—essential for meeting the growing global demand for clean water.
Meet the Mind Behind the Study
Led by Dr. Tamar Segal-Peretz and Dr. Guy Ramon, alongside Prof. Manish Kumar and a team of dedicated researchers, the study dives deep into the intricate world of membrane technology. Notably, Ph.D. student Chenhao Yao and former Technion student Dr. Adi Ben-Zvi played pivotal roles in this research, with Dr. Ben-Zvi now advancing her career as a postdoctoral researcher at Rice University.
A Global Water Crisis and the Role of Desalination
With approximately 25% of the global population lacking safe drinking water, the importance of desalination has never been clearer. As outlined by the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, technologies for water reuse and desalination are crucial—especially in drought-prone areas like Israel, where advanced desalination plants now provide around 70% of the nation’s water supply and 85% of wastewater is recycled for agriculture.
The Science of Reverse Osmosis Explained
Reverse osmosis (RO) is the cutting-edge technology driving modern desalination. This process forces water from a concentrated solution—such as seawater—through a selectively permeable membrane to produce pristine freshwater. Despite its widespread usage, the relationship between membrane structure and function remains poorly understood due to the membranes' incredibly intricate structures.
Mapping Membrane Structures for the Future
In their quest to unlock the secrets of membrane functionality, the research team employed advanced cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy (cryo-TEM) to achieve detailed 3D mappings of membranes in hydrated states—conditions that accurately reflect the operational realities of reverse osmosis.
A Major Leap in Membrane Design and Performance
One of the most remarkable findings was that water dramatically expands the membrane’s volume by over 30%. This revelation challenges previous assumptions based solely on dry-state analyses, marking a significant advancement in scientific understanding. The newly obtained nanometric mappings are poised to dramatically inform future advancements in membrane technology, driving the next wave of improvements in desalination and water reuse.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)