Revolutionizing Colorectal Cancer Predictions: How AI is Changing the Game
2025-04-18
Author: Wei
Background and Importance
Colorectal cancer (CRC) stands as one of the most common and lethal forms of cancer globally. Early detection of metastasis can dramatically improve patient outcomes, preventing the disease from reaching advanced stages. This groundbreaking research aims to harness cutting-edge machine learning (ML) techniques to enhance the predictability of metastasis among CRC patients, moving beyond previous methods by incorporating a comprehensive mix of demographic, lifestyle, nutritional, and clinical factors.
Study Insights
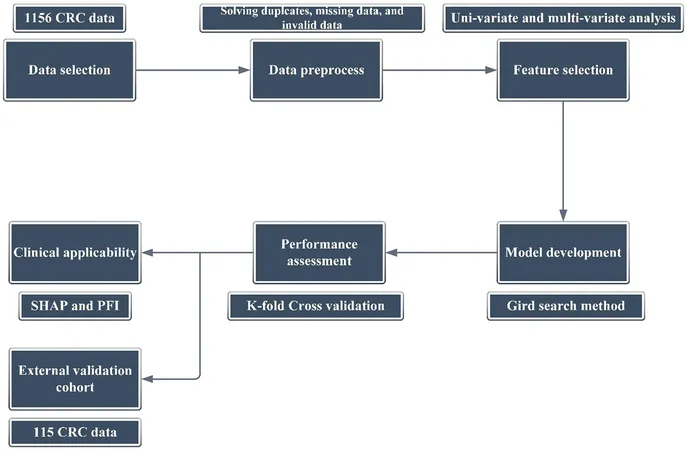
In a retrospective analysis of 1,156 CRC patients from Tehran's Masoud internal clinic (2017-2023), several advanced machine learning algorithms were deployed. Techniques like LightGBM, XG-Boost, and neural networks were tested to establish models capable of accurately predicting metastatic outcomes. Notably, LightGBM emerged as a standout performer, boasting exceptional predictive metrics—97% positive predictive value and an accuracy rate of over 88%. Factors such as the history of inflammatory bowel disease, family history of CRC, tumor size, and fruit intake were identified as key indicators of metastasis.
Outstanding Results
The LightGBM model delivered impressive results with a sensitivity of 83% and specificity of 93%. This indicates a robust ability to accurately predict which patients are likely to experience metastasis. External validation using data from another clinical center reaffirmed these findings, providing further credence to the model's reliability across different patient populations.
The Significance of Machine Learning in Cancer Care
Machine learning possesses the potential to transform oncology by offering predictive insights that can assist clinicians in tailoring treatment strategies. Previous endeavors in using ML for CRC outcomes have shown promise, but this study pushes the boundaries further by integrating an array of lifestyle and nutritional factors alongside traditional clinical indicators.
Future Perspectives and Recommendations
Despite its promising results, this study acknowledges some limitations. The data was sourced from a single clinical center, which may affect the model's generalizability across diverse populations. Future research is encouraged to incorporate broader datasets from multiple clinical sites and include genetic and radiomic data to enhance predictive power.
Conclusion
This innovative approach to predicting CRC metastasis using machine learning not only opens doors for early detection but also stands to significantly improve patient outcomes. The empirical findings illustrate that ML tools, like LightGBM, can serve as invaluable assets for oncologists, guiding informed decisions and paving the way toward better prognosis in colorectal cancer management.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)