Revolutionary Treatment Shows Promise for Hepatitis B Patients with Liver Failure
2025-08-29
Author: Jia
The Rising Threat of Liver Failure from Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a leading cause of liver failure globally, especially in cases of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). As antiretroviral therapy (ART) has transformed HIV treatment, co-infection with HBV can significantly worsen liver health, complicating prognosis and treatment.
Understanding the Clinical Dangers of ACLF
ACLF is alarmingly severe, with short-term mortality rates soaring between 50% and 90%. This critical condition arises when chronic liver disease flares, causing severe acute liver injury alongside complications like infections and organ failure—creating an urgent need for effective therapies.
Innovative Treatment Approach: Plasma Exchange and Perfusion
Artificial liver support systems (ALSS) play a crucial role in managing liver failure. In China, one effective approach combines plasma exchange (PE) and plasma perfusion (PP), particularly useful in treating HBV-related ACLF. This technique notably shows promise for HIV-negative patients, improving their short-term outcomes.
Limited Focus on the Co-infection Factor
Despite the crucial need for effective treatments, little attention has been given to HBV-ACLF patients co-infected with HIV. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of combined PP and PE therapy in both HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients with ACLF, shedding light on treatment outcomes.
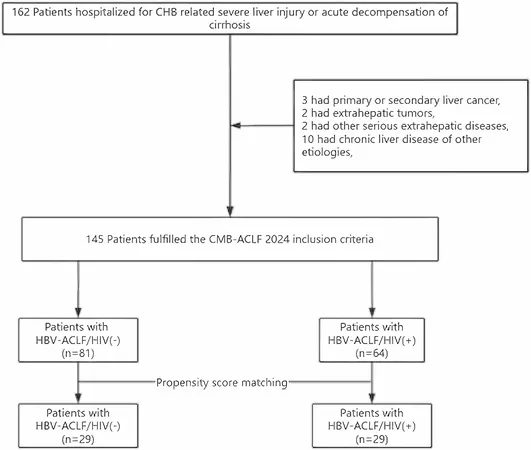
Patient Analysis: A Closer Look
This study analyzed 145 patients admitted for ACLF treatment between 2019 and 2025, including both HBV-ACLF/HIV(+) and HBV-ACLF/HIV(-) groups. Through rigorous evaluation, the researchers compared treatment responses, seeking to uncover differences that could influence therapy strategies.
Effective Treatments Show Promising Results
Patients from both groups received comprehensive medical care, with the combination of PP and PE treatments proving effective. Noteworthy improvements were observed in liver function indicators post-treatment, showcasing the significant benefits of this dual approach.
Survival Insights and Prognostic Factors
Survival analysis revealed no significant differences in short-term morbidity or mortality between the two patient groups, suggesting that the combined treatment methods equally benefit patients regardless of HIV status—a hopeful indicator for future therapies.
Addressing the Challenges Ahead
While this study emphasizes the efficacy of PP and PE in treating HBV-ACLF with and without HIV co-infection, challenges remain. Adverse reactions to treatment were recorded, necessitating vigilant monitoring, especially concerning bleeding complications in HIV-infected patients.
Towards a Brighter Future in Liver Disease Management
This groundbreaking research underlines the necessity for refined treatment protocols and increased awareness regarding HBV and HIV co-infection management. Future studies should explore the underlying mechanisms of treatment effectiveness to tailor therapies better, offering hope for higher survival rates and improved quality of life for these patients.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)