Revolutionary Study: Abbreviated MRI May Outshine Traditional Methods in Detecting Prostate Cancer!
2025-09-11
Author: Arjun
Could a Game-Changer Be on the Horizon for Prostate Cancer Detection?
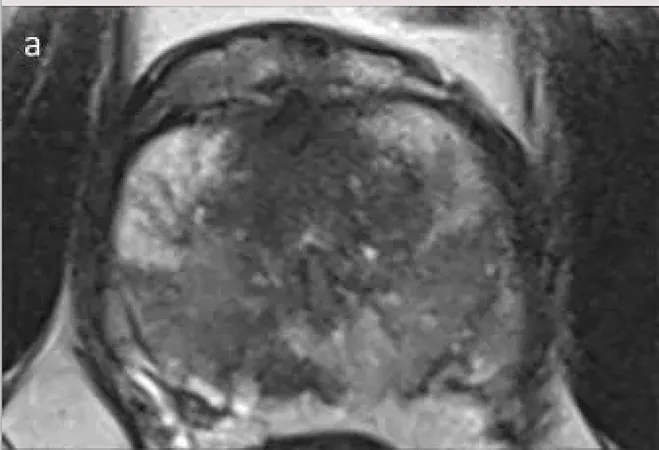
A groundbreaking multicenter study has sparked excitement in the medical community, with hopes that abbreviated biparametric magnetic resonance imaging (bpMRI) could potentially become the new gold standard for detecting prostate cancer (PCa). This research was recently unveiled in the prestigious Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
Study Insights: Head-to-Head Comparison of Imaging Techniques
The study involved an impressive cohort of 490 men, all with a heightened suspicion of prostate cancer, averaging 65 years in age and with a median PSA level of 5.6. Participants came from 22 centers across 12 countries, providing an extensive and diverse data set for analysis. Researchers compared the effectiveness of abbreviated bpMRI—which includes T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI)—against the more traditional multiparametric MRI (mpMRI).
Stunning Results: Similar Detection Rates!
The findings were remarkable: abbreviated bpMRI detected clinically significant PCa in 29.2% of cases, only slightly lower than mpMRI's 29.6%. Moreover, both methods displayed strikingly similar performance metrics: sensitivity (bpMRI: 98%, mpMRI: 99.3%), specificity (bpMRI: 61.6%, mpMRI: 60.1%), positive predictive value (PPV) (bpMRI: 53.1%, mpMRI: 52.5%), and negative predictive value (NPV) (bpMRI: 98.6%, mpMRI: 99.5%).
No Increase in Overdiagnosis or Biopsy Rates!
One of the most reassuring aspects of the study was the confirmation that bpMRI does not lead to an increase in the diagnosis of clinically insignificant cancer nor a rise in biopsy recommendations. This addresses prior concerns regarding the potential downsides of omitting contrast agents, as highlighted by lead researcher Alexander Ng, MBBS of University College London.
Three Major Takeaways!
1. **Comparable Diagnostic Accuracy:** Abbreviated bpMRI holds its own against traditional mpMRI with nearly identical detection rates for significant cancer and similar performance metrics. 2. **No Overdiagnosis or Increased Biopsies:** The study found that bpMRI does not lead to higher rates of unnecessary cancer diagnoses or biopsies, alleviating previous worries about contrast usage. 3. **Practical Benefits:** Encouragingly, bpMRI provides shorter scan times, eliminates the need for gadolinium contrast, boosts patient throughput, and minimizes costs and risks for healthcare providers.
Potential Impact on Prostate Cancer Imaging!
Given that around four million prostate MRI exams are conducted annually in the U.S., the implications of embracing an abbreviated bpMRI protocol are significant. Researchers highlighted its advantages in terms of accessibility, efficiency, and patient safety.
Conclusion: A Bright Future Ahead!
As we stand on the verge of a potentially transformative approach to prostate cancer detection, Ng and his colleagues emphasize the myriad benefits of bpMRI, including its reduced environmental impact and the elimination of unnecessary medical procedures. While the study recognized limitations regarding potential biases in cancer detection, the promise of a more efficient, effective, and safer method of diagnosis could change the landscape of prostate cancer screening.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)