Revolutionary Software Uncovers Hidden Aging Cells Linked to Diseases—A Game Changer for Healthcare!
2025-03-25
Author: Yu
Introduction
When it comes to human health, problematic aging cells are emerging as a significant concern. These prematurely aged cells cease normal growth and function, leading to serious health issues including cardiovascular diseases, Alzheimer's disease, and other chronic health conditions. The challenge lies in their elusive nature—identifying these cells has been akin to finding a needle in a haystack using conventional scientific methods.
Breakthrough Discovery of SenePy
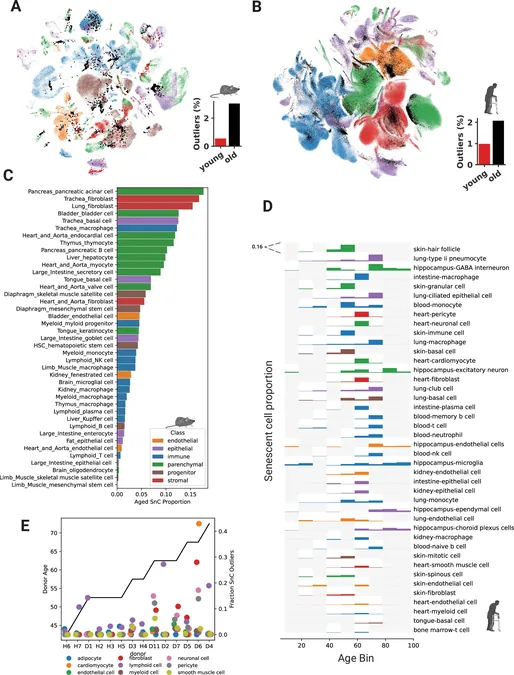
In a promising breakthrough, doctoral student Mark Sanborn from the University of Illinois Chicago has unveiled a cutting-edge software platform named SenePy, designed specifically for identifying aging—or senescent—cells across various organs and tissues. This groundbreaking tool, discussed in a recent publication in Nature Communications, promises to significantly enhance research capabilities concerning these biologically important cells.
Insights from Dr. Jalees Rehman
Dr. Jalees Rehman, the lead author and a prominent figure in the College of Medicine, emphasizes the impact of cellular senescence—the state where cells become dormant yet do not die. "This state is problematic as senescent cells fail to be replaced by healthy ones, leading to inflammation and disrupting the function of adjacent cells," said Dr. Rehman, who is also involved with the University of Illinois Cancer Center.
Research Methodology and Findings
To create SenePy, Sanborn meticulously analyzed single-cell sequencing data from over 1.6 million human and mouse cells. His efforts revealed that the genetic signatures of aging cells vary across different tissues—highlighting the complexity in identifying senescent cells. In total, the research team identified 72 distinct genetic signatures in mice and 64 in humans, demonstrating the nuanced differences in aging cell profiles.
Utility of SenePy for Researchers
SenePy serves as a vital tool for researchers, enabling them to analyze their own tissue samples against the extensive database of signatures compiled by the UIC team. The platform, being open-source, is freely accessible to the scientific community, fueling hopes of widespread usage and future therapeutic advancements. "The goal is for more researchers to harness this tool, ultimately leading to significant breakthroughs in treatment strategies," stated Sanborn.
Implications in Disease Research
The team's research employed SenePy to explore the implications of senescent cells in various diseases, including cancer, heart attacks, and even complications arising from COVID-19. "Our findings indicated that senescent cells tend to cluster. When one cell enters premature senescence, it can instigate dysfunction in neighboring cells," Dr. Rehman noted. The platform also provided insights into how senescence might act as a natural brake against tumor development, with elevated activation of cancer-promoting genes correlating to increased senescent scores.
Potential for Senolytic Drugs
Moreover, the researchers examined the potential of senolytic drugs—therapeutics aimed at eliminating senescent cells—to counteract disease and aging. "With an array of specific markers for various types of senescence across different cell types, we have the groundwork for developing new senolytic drugs targeting these cells," added Sanborn.
Broader Implications for Health
The implications of SenePy's development are vast, as the continued research may lead to pivotal advancements in combating age-related diseases and improving overall health outcomes. Additional co-authors from UIC contributing to this promising research include Xinge Wang, Shang Gao, and Yang Dai.
Conclusion
In a world increasingly focused on longevity and enhanced health, tools like SenePy could revolutionize our approach to understanding aging at the cellular level—paving the way for healthier futures!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)