Revolutionary Satellite Mapping Reveals Secrets of Seasonal Changes
2025-09-02
Author: Wei
Unlocking Nature's Calendar with Satellite Technology
For eons, humans have diligently recorded the subtle seasonal shifts that dictate the fate of crops. But now, technology has joined the observation, as a groundbreaking study published in *Nature* unveils how satellites are mapping the intricacies of seasons worldwide.
A New Perspective on Botanical Patterns
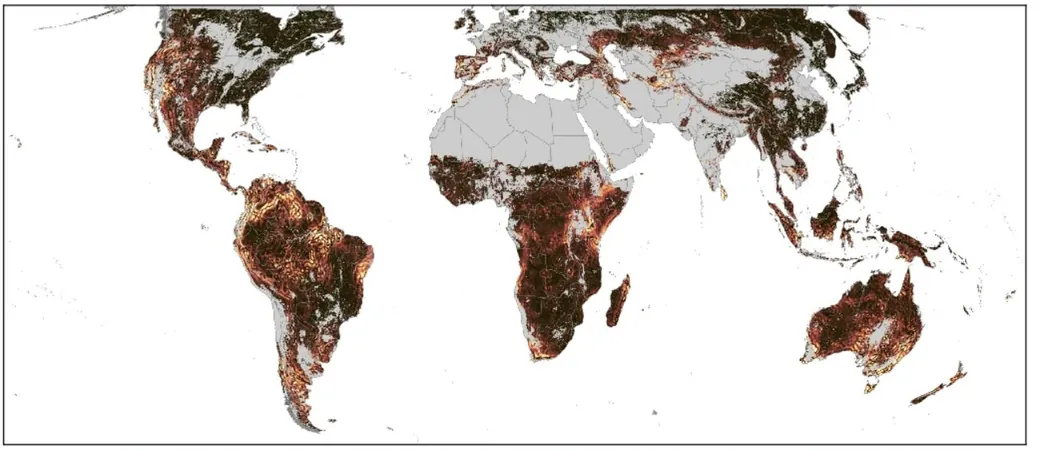
The most straightforward way to track seasonal changes across the globe is to observe Earth from above and monitor vegetation. Picture this: during winter, the northern regions of North America appear drab and gray. But when spring arrives, vibrant greens sweep in from the south as nature awakens with renewed vigor. Trees flourish, flowers bloom, and soon, autumn’s fiery hues return—echoing the cycle of life and death in nature.
However, this traditional method falters in areas characterized by extreme aridity or eternal greenery, such as the Amazon Rainforest or tropical climates. How do you assess seasonal transitions where the foliage remains lush all year?
Understanding Plant Stress for Seasonal Insight
This innovative study employs a novel approach: assessing how much plants are growing in specific areas. By utilizing methods from agriculture and ecology, researchers monitored solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence. This fascinating phenomenon occurs when plants engage in photosynthesis, releasing red light in precise frequencies, corresponding to their health. Stressed plants show reduced photosynthesis efficiency, making this metric invaluable for tracking seasonal changes.
Adding to this, the study looked at near-infrared observations of vegetation reflectivity—measuring how much sunlight plants absorb versus what they bounce back. Healthy plants reflect a greater amount of near-infrared light. By combining these techniques, researchers gained insights into plant health across even the ever-green landscapes.
A Paradigm Shift in Seasonal Mapping
The findings revealed that predicting seasons involves more than just geographical latitude. For instance, regions like the floodplains of the Amazon don't experience two distinct seasons but rather are shaped by singular dramatic events—like annual flooding—that dictate vegetation changes.
Moreover, the researchers discovered an intriguing phenomenon: adjacent areas with similar climates often experience seasonal discrepancies. This asynchronicity frequently arises near mountain ranges, which disrupt airflow and weather patterns, creating localized climates. A prime example is the stark contrast between Phoenix and Tucson in Arizona; while Tucson enjoys summer monsoons, Phoenix endures sweltering, desolate heat.
The Implications of Seasonal Variability
These groundbreaking findings lend credence to the hypothesis that heightened local seasonal variability fosters biodiversity. If a species inhabits both Tucson and Phoenix, variations in seasonal cues—like when it rains—could lead to different mating times. Over generations, this could potentially result in speciation.
This research, although still a developing theory, supports the notion that tropical regions, rich in biodiversity, demonstrate increased local variability in seasonal patterns—a conclusion that aligns perfectly with this innovative study's outcomes.
With these revolutionary mappings, scientists may now better understand the world’s complex ecosystems, unveiling how they change and evolve even in the most subtle ways.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)