Revolutionary Robotic Cilia Technology Could Transform Airway Disease Monitoring!
2024-11-11
Author: Jia
Keeping a close eye on airway conditions is crucial, especially for patients undergoing treatment for lung cancer and other respiratory diseases. The timely detection of changes can make all the difference when it comes to effective interventions, particularly when airway stents are utilized to alleviate central airway obstructions. However, monitoring vital biomarkers like mucus conditions—indicators of inflammation and stent patency—has historically been a challenge due to the limitations of current methods.
Traditional monitoring techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) imaging and bronchoscopic inspections, come with risks including radiation exposure and an inability to provide continuous, real-time feedback from home. Thankfully, a groundbreaking approach has emerged from a team of researchers at Vanderbilt University School of Engineering in Nashville, TN. They have created an innovative system utilizing artificial cilia to monitor mucus conditions in the airways. This technology promises a more effective means of detecting infections, airway blockages, and assessing the severity of conditions like cystic fibrosis (CF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer.
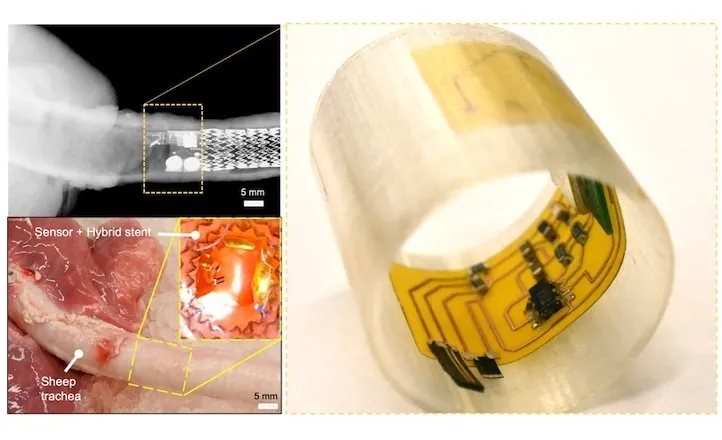
In a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the researchers demonstrated a novel technology that mimics the sensing abilities of biological cilia to assess critical mucus characteristics such as viscosity and layer thickness—two vital biomarkers that can indicate the progression of disease. To measure mucus viscosity, their sensing mechanism employs external magnetic fields to actuate a magnetic artificial cilium, which then detects changes in its shape using a flexible strain gauge.
Moreover, the research team has developed an advanced cilium equipped with capacitance sensing capabilities to accurately gauge mucus layer thickness. Unique features make this technology stand out, including self-calibration, adjustable sensitivity, and an extended operational range—all powered by an external magnetic actuation system that can be worn by the patient. The sensors were rigorously tested, both individually and alongside airway stents, in controlled laboratory settings as well as sheep trachea models. Impressively, the sensors wirelessly relay the collected data to a smartphone or cloud platform, allowing for thorough analysis and prompt disease diagnosis.
“The proposed sensing mechanisms and devices pave the way for real-time monitoring of mucus conditions, facilitating early disease detection and providing stent patency alerts,” the researchers noted in their study. This technological advancement opens the door for timely interventions and personalized care for patients suffering from airway diseases, which could lead to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
With this innovative technology on the horizon, the future of airway disease management looks brighter than ever! Keep an eye on this space as continuous developments could bring life-saving solutions to millions worldwide.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)