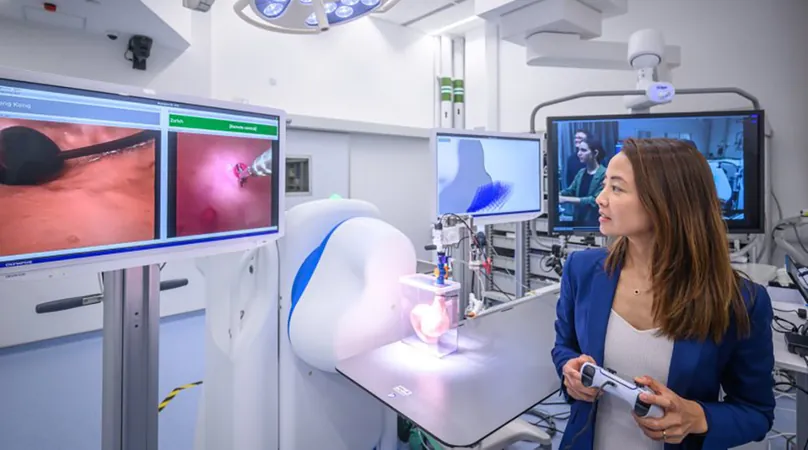
Revolutionary Remotely Controlled Robot Redefines Endoscopy Procedures
2024-09-30
Author: Nur
Introduction
A groundbreaking advancement in medical technology is set to revolutionize endoscopy with the introduction of a new remotely guided, magnetically steered robotic endoscope. This innovative device promises to facilitate deeper explorations within the human body, making procedures safer and less invasive. Its potential application spans even to remote regions that lack trained medical personnel, thus enhancing healthcare accessibility for underserved areas.
Understanding Endoscopy
Endoscopy—a minimally invasive procedure—utilizes a long, flexible tube with a camera, allowing doctors to visually examine the gastrointestinal tract. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), the United States sees over 20 million gastrointestinal endoscopies performed annually, aiding in the diagnosis of various conditions including swallowing disorders, inflammation, ulcers, and cancers.
Challenges and the Solution
However, traditional endoscopy requires years of training—skills that are often inaccessible in many parts of the world. This shortage of qualified surgeons can limit patient access to vital diagnostics and treatments. Enter teleoperated robotic systems, which allow surgeons to conduct procedures from a distance using advanced robotics.
The Remote Operation Study
A recent study published in Advanced Intelligent Systems highlighted the successful remote operation of an endoscope from Zurich to Hong Kong. This teleoperated system transmits live video and joystick commands over a secure internet connection, enabling real-time control. Quentin Boehler, a leader in medical robotics at ETH Zurich, expressed enthusiasm over the technology, stating, “This system enhances precision, reduces the physical burden on surgeons, and democratizes access to surgical expertise worldwide.”
How It Works
The robotic endoscope is designed with magnets distributed along its body. By creating a magnetic field with a nearby device, surgeons can effectively navigate the endoscope within the patient's body using joystick controls. Boehler's team commenced their experiments on synthetic models mimicking the human gastrointestinal tract, progressing to real-life scenarios with sedated pigs due to the physiological similarities.
Trial Success
The team's trials proved successful, successfully guiding the endoscope within the pig's stomach from nearly 5,700 miles away, with minimal operator delay. Boehler noted that achieving complex maneuvers, including taking biopsies, underscored the system’s reliability.
Future Aspirations
With aspirations of introducing this advanced technology into human clinical settings, Boehler and his colleagues are exploring additional applications, including neurovascular interventions. These areas present critical opportunities to leverage the endoscope's flexibility and precision, particularly in treating life-threatening conditions like acute ischemic strokes.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the promise of this innovation, the rollout of teleoperated robotic surgery will depend on reliable, low-latency internet access, especially in lower-income regions, where infrastructure challenges can impact implementation. Boehler acknowledged, “It requires significant time and effort to refine these technologies to meet the practical demands of medical professionals.”
Collaborative Efforts
The development of this robotic technology also stems from the collaborative efforts of a spin-off company, Nanoflex Robotics, which aims to bridge research and clinical application. As remote surgeries become more feasible, we stand on the brink of a transformative era in medicine, where healthcare delivery can transcend geographical barriers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of teleoperated robotic endoscopes holds the key to not only enhancing the safety and efficiency of medical procedures but also revolutionizing access to healthcare worldwide. As the journey from laboratory to clinic unfolds, the potential to save lives and streamline surgeries is more exciting than ever. Stay tuned as we witness the future of medical robotics taking shape!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)