Revolutionary Protein Takes Tissue Regeneration to the Next Level!
2025-09-15
Author: Li
Groundbreaking Innovation in Biomaterials
A powerful collaboration between researchers at POSTECH and Inha University has resulted in a groundbreaking biomaterial set to transform tissue regeneration forever!
Unlocking the Power of Elasticity
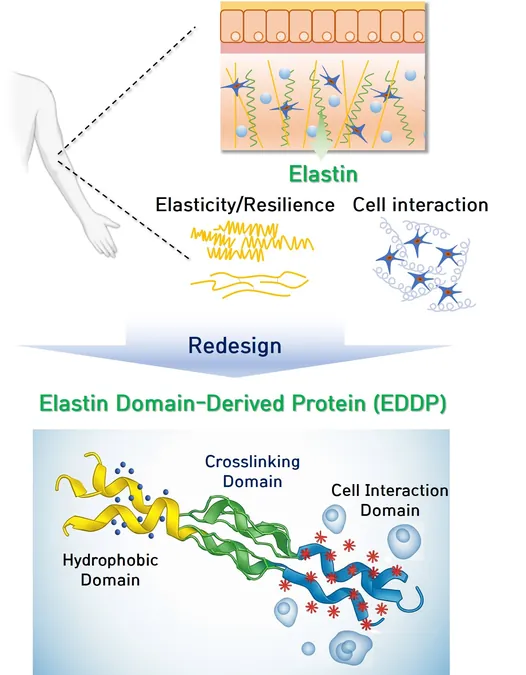
At the heart of this discovery lies elastin, a natural protein known for its incredible ability to stretch and snap back—much like a rubber band. This remarkable property keeps our lungs functioning smoothly, allows our blood vessels to pulse with each heartbeat, and helps our skin maintain its youthful elasticity.
Facing the Challenges of Natural Elastin
Despite its amazing qualities, harnessing natural elastin for medical use has been fraught with difficulties. It’s scarce, hard to purify, and poses risks of immune reactions when taken from other individuals. In an effort to conquer these challenges, scientists have experimented with elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs). While these synthetic alternatives can be mass-produced, they fall short of mimicking the intricate functions of natural elastin.
Meet the Game-Changer: EDDP
The innovative research team has now achieved a major breakthrough by developing a novel protein called elastin domain-derived protein (EDDP). By handpicking and reassembling the essential components of tropoelastin, the precursor to elastin, they've crafted a protein that beautifully balances functionality and production.
A Triple Threat for Regeneration
EDDP boasts a remarkable combination of features: a hydrophobic domain for superior physical properties, a cross-linking domain for enhanced stability, and a cell-interaction domain that fosters crucial cell connections. This trifecta not only enables mass production but also allows EDDP to rival natural elastin in both elasticity and resilience.
Boosting Cell Growth and Survival
What sets EDDP apart is its ability to promote cell adhesion and growth. Unlike conventional ELPs, EDDP emits powerful signals that encourage cell survival, making it a standout choice for regenerating damaged tissues effectively.
A Bright Future for Medical Applications
Professor Hyung Joon Cha from POSTECH couldn't contain his excitement about the potential applications of EDDP. He highlighted its role in regenerating vital tissues such as heart valves, damaged blood vessels, and even torn ligaments. This revolutionary protein is poised to reshape the future of medical treatments, creating new hope for countless patients.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)