Revolutionary OLED Technology Promises Sleek, Lightweight Night Vision Glasses!
2024-09-17
Introduction
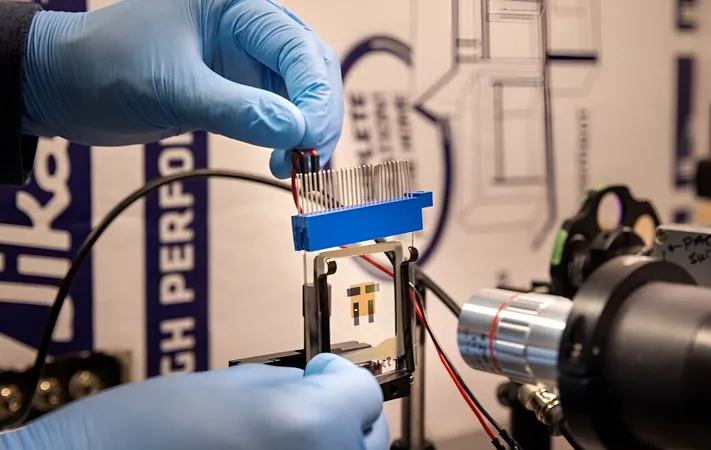
Imagine a future where heavy, cumbersome night vision goggles are replaced by sleek, lightweight glasses. Researchers from the University of Michigan have developed a groundbreaking new OLED (organic light emitting diode) technology that could make this dream a reality. Their findings, published in the prestigious journal *Nature Photonics*, could revolutionize not only personal night vision but also bring down costs and enhance the practicality of such devices for extended use.
Current Night Vision Technology
Current night vision technology relies on bulky image intensifiers that can weigh down users and drain their batteries. These systems convert near-infrared light into electrons, which are then accelerated through a series of tiny channels to produce visible light. This time-consuming and inefficient process amplifies the incoming light roughly 10,000 times.
Breakthrough OLED Technology
In contrast, the new OLED technology efficiently converts near-infrared light into visible light with more than 100 times amplification—all while being lightweight and operating on significantly lower voltages.
Key Features of the OLED Device
One standout feature of this innovative OLED device is its ability to operate within an ultra-thin film stack measuring less than a micron thick—much thinner than a human hair. "One of the most attractive features of this new approach is its minimal thickness,” said Chris Giebink, a leading professor in the study. This ultra-thin construction not only enhances portability but also contributes to dramatic reductions in power consumption, potentially extending battery life for users in the field.
Device Structure and Efficiency
The device's unique structure integrates a photon-absorbing layer that captures infrared light and a five-layer stack of OLEDs. This system converts electrons produced in the photon-absorbing layer into visible light photons. In an impressive display of efficiency, the device can generate up to five photons for every incoming electron, drastically increasing efficiency compared to traditional methods that only allow a one-to-one ratio.
Advanced Image Processing
Additionally, this next-generation OLED incorporates a fascinating feature known as hysteresis, or a memory effect. This enables the device to maintain light output based on past illumination—potentially mimicking some functions of the human visual system. While this capability poses unique challenges for traditional night vision applications, it could pave the way for advanced image processing techniques. Imagine a night vision system that not only helps you see but can interpret and classify images in real time, much like our brains do!
Widespread Adoption and Future Prospects
The University of Michigan team emphasized that the materials and fabrication methods used for this OLED technology are readily available in the market, suggesting that widespread adoption could be on the horizon. This development could make night vision optics not only more accessible and cost-effective but also empower various fields such as security, outdoor recreation, and even medical applications.
Conclusion
The future of night vision is bright, and with the advent of this revolutionary OLED technology, users could soon experience an unprecedented combination of performance and comfort. Stay tuned for updates, as this could be the dawn of a new era in visual technology!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)