
Revolutionary Neuromorphic Computing Takes Robotic Navigation to New Heights!
2025-06-23
Author: Nur
Breakthrough Technology From Queensland University of Technology
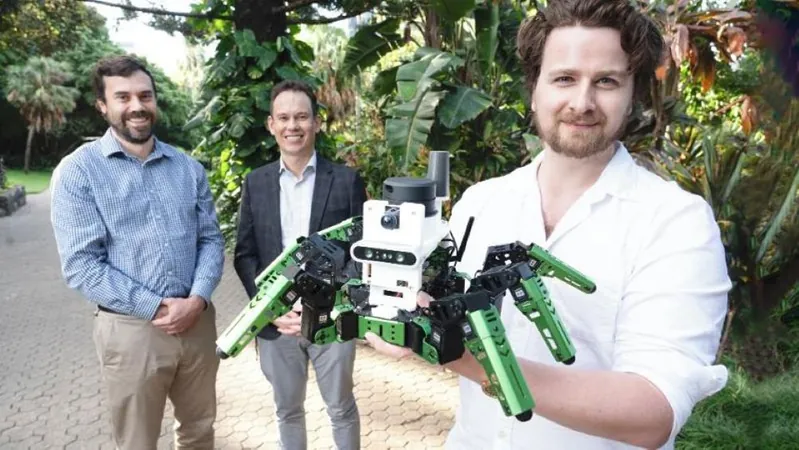
A groundbreaking innovation at the Queensland University of Technology (QUT) is transforming robotic navigation with a new system called LENS (Locational Encoding with Neuromorphic Systems). This cutting-edge technology uses brain-inspired computing methods to dramatically reduce energy consumption in robotic place recognition.
Meet the Brilliant Minds Behind LENS
Led by neuroscientist Dr. Adam Hines, along with esteemed colleagues Professor Michael Milford and Dr. Tobias Fischer, the QUT Centre of Robotics team has made significant strides in neuromorphic computing, as detailed in the prestigious journal Science Robotics.
A Game Changer for Energy Efficiency
Dr. Hines explains that traditional energy demands present a significant hurdle in real-world robotics, particularly in critical missions such as search and rescue, space exploration, and underwater navigation. Thanks to LENS, these challenges may soon be a thing of the past: the system can slash energy requirements for visual localization by a staggering 99%, allowing robots to operate longer and travel farther on limited power.
Record Breaking Storage Efficiency
In a remarkable test, LENS successfully recognized various locations over an 8km journey while utilizing a mere 180KB of storage—almost 300 times less than conventional systems. This efficiency sets a new standard in robotic technology.
The Brains Behind the Operation
LENS integrates a sophisticated spiking neural network with a movement-sensitive camera and a low-power chip, all compactly housed within a small robot. According to Dr. Hines, "This system exemplifies how neuromorphic computing can enable real-time, energy-efficient tracking for robots, paving the way for groundbreaking low-power navigation technologies."
The Secret Sauce: Novel Algorithms
Dr. Fischer, an ARC DECRA Fellow, highlights a pivotal innovation in LENS: a new algorithm that leverages two types of advanced bio-inspired hardware. By employing a unique 'event camera' that captures changes and movements at microsecond intervals, LENS closely mimics human visual processing, ensuring robots can achieve effective visual place recognition.
A Future of Limitless Exploration
As energy consumption decreases, remotely operated robots will be empowered to venture farther and for longer periods. By relying solely on visual information for localization in a fast and efficient manner, LENS is set to revolutionize how robots navigate our world—making the once impossible, possible!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)