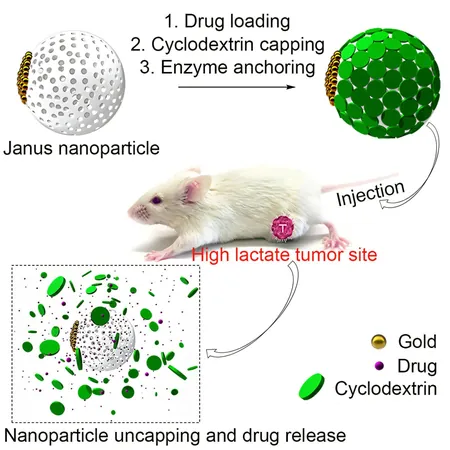
Revolutionary Nanoparticle System Targets Cancer Cells with Precision: A Game Changer for Chemotherapy
2025-07-01
Author: Jia
A Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unveiled a cutting-edge nanoparticle-based system that promises to revolutionize chemotherapy by delivering potent anti-cancer drugs directly to cancer cells, sparing healthy tissue and significantly reducing toxic side effects. This innovative approach could allow clinicians to administer more effective doses of chemotherapy, enhancing patient outcomes.
Understanding the Warburg Effect
Published in *Cell Reports Medicine*, the study explores a common metabolic quirk known as the "Warburg effect," which is pivotal in differentiating cancer cells from normal cells. Cancer cells, unlike their healthy counterparts, convert glucose into lactate instead of fully breaking it down for energy. This unique metabolism creates an environment ripe for targeted therapies.
"Some solid tumors can have lactate concentrations over 40 times higher than normal tissue," explains Dr. Xiaoyang Wu, the lead researcher and Associate Professor at the University of Chicago. This stark difference allowed the researchers to craft a drug delivery system that zeroes in on these lactate-rich zones.
Innovative Nanoparticle Design
The team's breakthrough involves tiny silica nanoparticles, which can be injected into the bloodstream filled with various cancer drugs. What sets these nanoparticles apart is a unique lactate-responsive switch that enables them to release their drug payload specifically in tumors rather than in healthy tissue.
The mechanism works like this: when the nanoparticles enter a lactate-rich tumor environment, an enzyme within them activates, breaking down lactate into hydrogen peroxide. This process dismantles a protective cap on the nanoparticle, allowing the drug to be released precisely where it’s needed.
Promising Results in Animal Models
Tested in mice with different types of cancer, this targeted system demonstrated remarkable efficiency. It released a tenfold higher concentration of the drug directly within tumors compared to traditional injection methods, resulting in slower tumor growth and improved survival rates for the test subjects.
Broad Applications Beyond Cancer
Notably, lactate is not only relevant in cancer treatment; elevated levels are also seen in inflammatory diseases such as arthritis. This nanoparticle platform could potentially be adapted to enhance the delivery of anti-inflammatory medications, opening new avenues for treatment across various conditions.
Taking Research to the Next Level
Determined to bring this promising technology to clinical settings, Dr. Wu co-founded Alnair Therapeutics through the Polsky Center for Entrepreneurship and Innovation. However, scaling up production for human trials remains a key challenge. The team is initially focusing on the well-established chemotherapy drug Doxil, with ambitions to apply this technology to other therapeutic agents in the future.
As Wu delves deeper into the metabolic peculiarities of tumors, he hopes to uncover further insights that could lead to innovative drug delivery methods and improved cancer therapies.
The Future of Cancer Treatment Looks Bright
With its targeted approach and minimal side effects, this innovative nanoparticle therapy could mark a significant advancement in the fight against cancer, offering new hope to patients and clinicians alike. As research continues, we may be on the threshold of a new era in precision medicine.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)