Revolutionary Miniature Lithium-Ion Battery Paves the Way for Breakthroughs in Biomedical Devices and Robotics!
2024-10-25
Author: Sarah
Revolutionary Miniature Lithium-Ion Battery Unveiled
A groundbreaking advancement from researchers at the University of Oxford has unveiled the world's smallest soft lithium-ion battery, potentially transforming the landscape of biomedical applications such as heart tissue repair and advanced robotics. This innovative study has been published in the prestigious journal *Nature Chemical Engineering*.
Meeting the Demand for Ultra-Small Devices
As the demand for ultra-small smart devices—measuring just a few cubic millimeters—increases, there arises a need for equally compact power sources that can seamlessly integrate into biological systems. Traditional batteries simply don't cut it; they need to be soft, biodegradable, and capable of interacting safely and efficiently with human tissues.
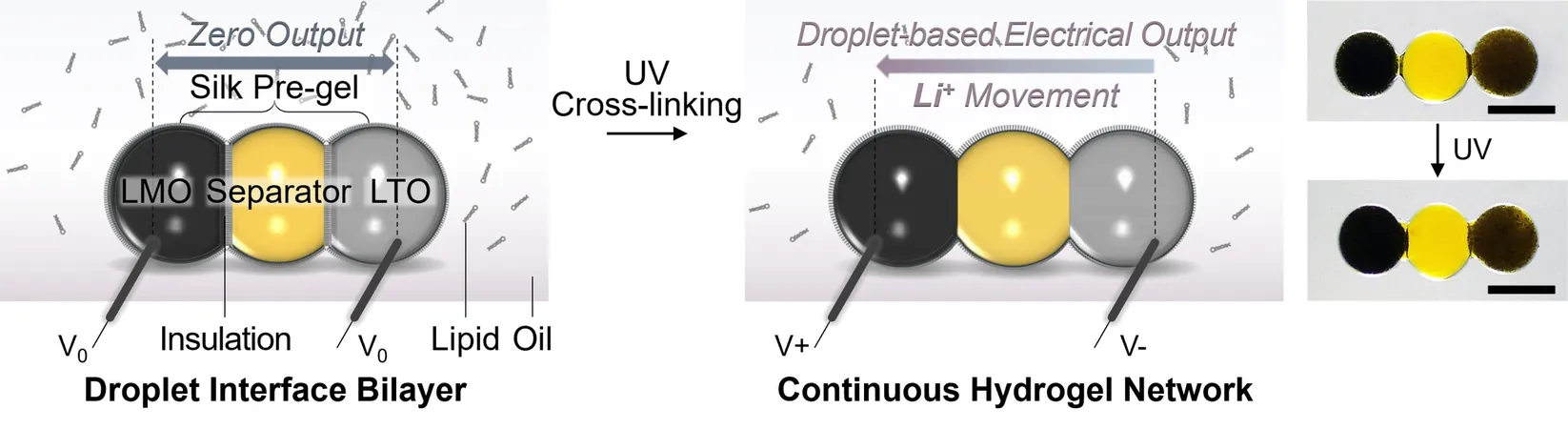
Innovative Design and Technology
The researchers, spearheaded by Dr. Yujia Zhang, have ingeniously created a miniature battery using biocompatible hydrogel droplets. This remarkable design features three microscale droplets, each with a minuscule volume of just 10 nanoliters, connected through a process known as surfactant-supported assembly. By employing lithium-ion particles, the battery generates dependable energy from its dual ends.
Revolutionary Qualities of the Droplet Battery
Dr. Zhang emphasized the battery's revolutionary qualities, stating, “Our droplet battery is not only light-activated and rechargeable but also becomes completely biodegradable after its use. As it stands, this is the smallest hydrogel lithium-ion battery with an exceptional energy density.
Laboratory Success and Future Applications
In a significant leap forward, this droplet battery powered vital interactions in the lab, such as moving charged molecules between synthetic cells and even controlling the rhythmic beating of mouse hearts. Additionally, by incorporating magnetic particles, the battery could serve as a mobile energy carrier, suggesting applications far beyond the initial biomedical scope.
Implications for Heart Health
Professor Ming Lei, a leading electrophysiologist specializing in cardiac arrhythmias, noted the implications for heart health: “With cardiac arrhythmia being a leading cause of death globally, our proof-of-concept tests in animal models represent a thrilling new paradigm for wireless and biodegradable solutions in arrhythmia management.
A Future of Biocompatible Electronic Devices
The research group leader, Professor Hagan Bayley, praised the work, highlighting that this tiny soft lithium-ion battery is the pinnacle of a series of microscale power solutions developed by Dr. Zhang. "This points to an incredible future for biocompatible electronic devices that are capable of functioning within the body's natural environment."
Conclusion: A New Era in Biomedical Engineering
As the boundaries between medicine and technology continue to blur, the innovative developments at the University of Oxford signify just the beginning of a new age in health management and biomedical engineering. With the potential to revolutionize how we treat cardiovascular issues and integrate small devices into our biological systems, this research could be a game-changer for the medical field! Stay tuned to see how this tiny powerhouse can reshape not only healthcare but the entire future of robotics!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)