
Revolutionary Method Could Enable Survival in Deep Space Using Moon Dust!
2025-07-23
Author: Nur
Space Exploration: A New Era Begins!
The dream of sending humans into deep space is inching closer to reality, thanks to groundbreaking engineering breakthroughs. However, the challenge of transporting vital supplies like water, oxygen, and fuel remains a monumental and costly endeavor—NASA estimates that just one kilogram of material can cost thousands of dollars!
A Game-Changing Discovery!
But hold onto your space helmets! A new study from a team of innovative researchers in China reveals that essential resources could be generated right in space. By harnessing sunlight, lunar soil, and—even more fascinating—astronauts' breath, scientists are working to slash costs and make space travel more feasible!
Lunar Soil: The Key to Water!
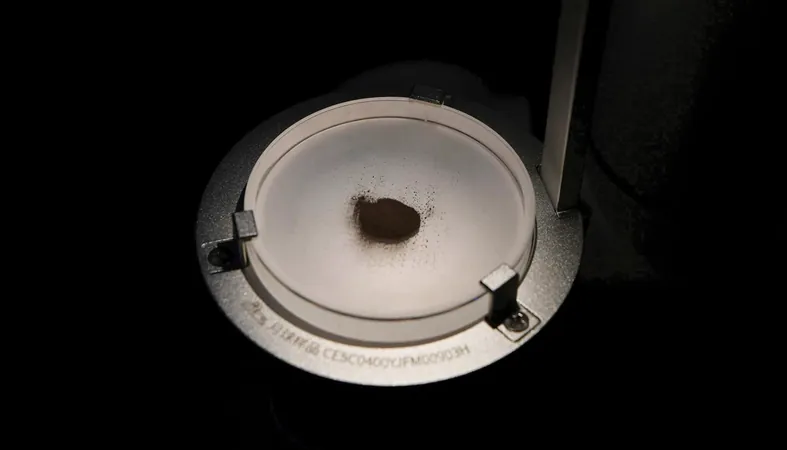
While it's well known that ice exists at the moon's frigid poles, accessing these regions is anything but easy. Thankfully, researchers have found an alternative way to produce water. Analyzing lunar soil samples from China's Chang’E-5 mission, they discovered that the mineral ilmenite can be heated to high temperatures. This process allows hydrogen from solar winds to react with the mineral, producing valuable water.
Solar Power: A New Resource from Extreme Conditions!
Building on this, a team led by Zhigang Zou and Yingfang Yao at Nanjing University, alongside Lu Wang from The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen, took things a step further. They used bright, simulated sunlight to heat lunar soil samples, enabling the ilmenite to release water. But that's not all—they also managed to utilize the extreme heat to split carbon dioxide from astronauts' breaths into carbon monoxide and oxygen, while also liberating hydrogen from water. This hydrogen could provide crucial fuel for spacecraft!
Sustainable Resources in an Untamed Frontier!
According to Matthew Shaw, an astrometallurgy expert, this innovative approach of using solar thermal energy represents a monumental shift away from traditional Earth-based resource extraction methods. However, he points out a potential downside: ilmenite's scarcity in certain lunar regions could limit the sustainability of this process.
The Future of Space Travel Awaits!
This research not only opens the door for more sustainable living conditions in space but also holds the promise of reducing reliance on Earth for essential supplies. As we prepare for the next giant leap for mankind, these developments in utilizing lunar resources might just pave the way for a new era of exploration and survival among the stars!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)