Revolutionary Method Boosts MnBi₂Te₄'s Topological Phases
2025-09-01
Author: Rajesh
Groundbreaking Advances in Material Science
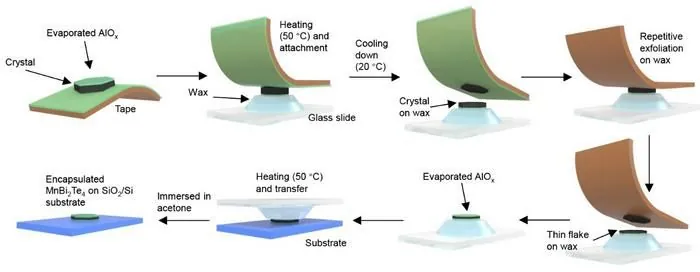
In a stunning breakthrough, the research team from Tsinghua University and RUC has unveiled a novel wax-assisted exfoliation technique that significantly enhances the properties of MnBi₂Te₄, an exciting material known for its topological phases.
Innovative Exfoliation Technique Revealed
This cutting-edge method employs a thermoplastic adhesive, Crystalbond 509, that transforms from a soft, viscous state under heat to a rigid, transparent solid upon cooling. By leveraging this unique characteristic, the researchers affixed MnBi₂Te₄ crystals onto heated wax, and as the wax cooled, it solidified into a protective shell. This innovative approach not only safeguarded the integrity of the crystals but also facilitated the creation of large-area, atomically flat flakes that are ideal for device fabrication.
Dual-Surface Encapsulation for Enhanced Performance
Building on previous studies that highlighted the advantages of a single AlOₓ capping layer for MnBi₂Te₄, the team advanced their work by crafting heterostructures where both surfaces of the MnBi₂Te₄ flakes are encapsulated with AlOₓ layers. This dual-surface encapsulation offers enhanced stability and performance, paving the way for next-generation electronic and spintronic applications.
Implications for Future Technologies
The implications of this research are monumental. The ability to produce high-quality MnBi₂Te₄ with improved properties could lead to remarkable developments in quantum computing, advanced electronic devices, and innovative spintronic technology—fields that hinge on the manipulation of electron spin as well as charge. Experts are keenly watching how this method could revolutionize the landscape of material science.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)