Revolutionary Long-Read Sequencing Technique Unveils Hidden Genetic Complexities in Rare Diseases
2024-11-04
Author: John Tan
Revolutionary Long-Read Sequencing Technique Unveils Hidden Genetic Complexities in Rare Diseases
A groundbreaking technique known as long-read sequencing is transforming the way chromosomal abnormalities are analyzed, revealing a level of genetic complexity previously hidden from conventional diagnostic methods. This exciting advancement comes from a team of researchers and clinicians in Sweden, pushing the boundaries of genetic research as published in the reputable journal *Genome Research*.
Enhanced Diagnostic Capability
For individuals suffering from rare diseases linked to intricate chromosomal issues, the traditional methodologies have often fallen short, resulting in ambiguous diagnoses. Long-read sequencing, however, allows scientists to read DNA sequences that are up to 50 times longer than those obtained via standard sequencing techniques. This enhanced capability provides a much clearer picture of the patient's genetic landscape, paving the way for more targeted and effective treatments.
Findings from the Swedish Research Team
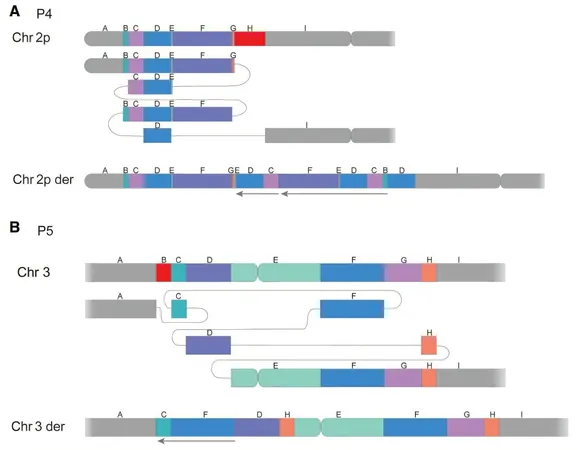
The Swedish research team, led by esteemed researchers from Karolinska Institutet and Uppsala University, analyzed clinical samples from patients with complex health conditions. The results were unexpected, revealing a significantly deeper level of chromosomal complexity across various abnormalities. "We were astonished by the findings. The intricacies uncovered far exceeded our initial expectations," stated Anna Lindstrand, Professor of Clinical Genetics at Karolinska Institutet and Chief Physician at Karolinska University Hospital.
Understanding the Nuance of Chromosomal Abnormalities
Interestingly, many patients harboring these complexities may exhibit no symptoms except for fertility challenges, while others may experience developmental delays. The nuance of these chromosomal abnormalities highlights the need for advanced diagnostics that take into consideration the diverse impacts these issues have on health.
Collaboration Enhances Research Outcomes
The collaborative effort involving multiple research centers across Sweden was pivotal to the success of this study. Lars Feuk, Professor at Uppsala University, emphasized, "The integration of researchers and clinicians from various genomic medicine centers has been essential." This multifaceted approach enabled a comprehensive examination of 16 samples from 13 families, contributing to a rich database of genetic information.
Utilization of Existing Biobanks
One of the remarkable implications of this research is that DNA samples previously prepared and stored under traditional conditions can now be used for long-read sequencing. This crucial adaptability positions the new technology for easier implementation in clinical settings, optimizing the use of existing biobanks to save both time and financial resources.
Forging a New Era of Diagnostics
In response to the detailed data extracted from long-read sequencing, researchers have developed a specialized bioinformatics analysis pipeline that supports the interpretation of intricate genetic variants. "We have constructed a user-friendly pipeline essential for piecing together the complexities of chromosomal aberrations," remarked first author Jesper Eisfeldt from the Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery at Karolinska Institutet.
Looking Ahead: Cost and Accessibility
Despite lingering concerns regarding the cost of long-read sequencing compared to traditional methods, the researchers are optimistic. They predict that within five years, this technique will become a standard practice in diagnosing rare diseases, thanks to rapid advancements in technology that are making it more accessible.
The Future of Genetic Analyses
"There is an incredible acceleration in the capabilities of long-read sequencing technologies," explained Adam Ameur, a bioinformatician. He believes that as costs decrease and precision improves, more individuals will benefit from enhanced genetic analyses that can reduce the need for redundant testing, resulting in significant healthcare savings.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in Genomic Medicine
In conclusion, this pioneering study not only illuminates the complexities of chromosomal abnormalities but also points to a future where long-read sequencing is integrated into routine clinical practice, offering groundbreaking possibilities for the diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases. The journey toward implementation may be shorter than anticipated, marking an exciting new chapter in genomic medicine.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)