Revolutionary Insights into Fetal CMV Infection Screening: A Groundbreaking Study from China
2025-04-16
Author: Jia
Introduction to the Study
In a pioneering examination of fetal cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection screening, researchers from a moderately developed city in western China have unveiled startling data regarding prenatal diagnosis in pregnant women. This study involved nearly 58,000 expectant mothers and highlights critical findings about CMV IgM/IgG serology and fetal health.
Participants and Methodology
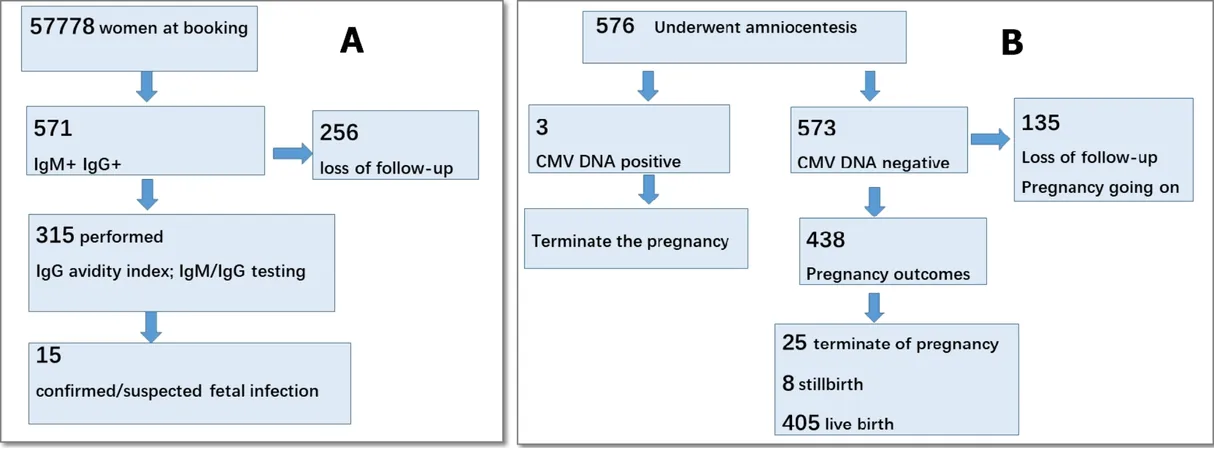
The study encompassed 57,778 pregnant women, with an average age of 29.88 years. The serological assessments revealed a striking 95.65% seroprevalence of CMV IgG antibodies, yet only 0.99% for IgM antibodies. Among those with positive IgM results, only a fraction confirmed recent infections, raising questions about the reliability of IgM as an indicator of active CMV.
Prenatal Diagnosis: The Crucial Amniocentesis
During the study, 576 women underwent amniocentesis and CMV PCR analysis as part of their prenatal care, aimed at identifying possible fetal infections based on ultrasound anomalies, particularly concerning the central nervous system. Alarmingly, only a small number of positive diagnoses were made despite the prevalence of certain ultrasound markers.
Confirmed Cases of Fetal Infection: The Eye-Opening Findings
Four notable cases of fetal CMV infection were documented, each revealing the dire consequences associated with the virus. For instance, one case led to pregnancy termination following severe fetal brain malformations detected via MRI and amniotic fluid analysis.
Fascinating Case Studies
- **Case 1** was revealed at 25 weeks with alarming brain abnormalities and eventually tested positive for CMV via amniocentesis, resulting in pregnancy termination. - **Case 2**, diagnosed with fetal growth restrictions, also exhibited CMV presence in amniotic fluid, leading to a similar decision. - **Case 3** had rising antibody levels and severe fetal ultrasound findings; despite attempts to monitor, this pregnancy concluded in termination as well. - Intriguingly, **Case 4** was initially deemed healthy until further testing uncovered latent CMV, illustrating the unpredictable nature of the virus.
Follow-Up and Birth Outcomes
After the series of prenatal tests and decisions on pregnancy terminations, a closer look into the 438 remaining pregnancies revealed critical outcomes. Most babies born under careful monitoring remained asymptomatic, although a small number faced hearing issues.
The Need for Enhanced Screening Techniques
This eye-opening study urges a reevaluation of how CMV infections are screened and diagnosed during pregnancy. Notably, high seroprevalence in the community might lead to missed diagnoses simply due to the limitations of current serological tests.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The research underscores the importance of comprehensive prenatal screenings that incorporate advanced diagnostic methods beyond traditional serology. As the field moves forward, future investigations should explore innovative techniques like cell-free DNA analysis in maternal blood, which has shown promising potential for early detection of CMV infections.
Final Thoughts
With the findings from this study, healthcare providers may adapt their strategies for CMV infection screening and management during pregnancy, prioritizing safer outcomes for both mothers and their babies.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)