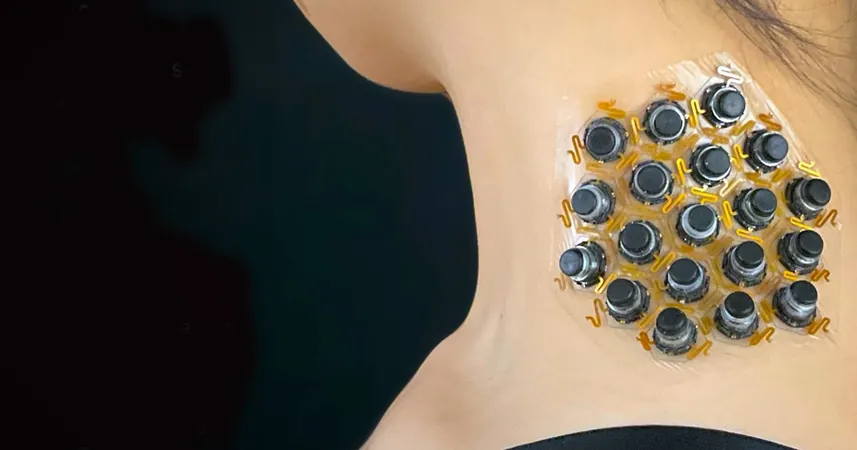

Revolutionary Haptic Patch Transforms Touch Sensations into Wearable Technology
2024-11-06
Author: John Tan
Why This Breakthrough Matters
This thin, flexible haptic patch adheres seamlessly to the skin, enhancing sensory experiences not only in the realms of gaming and virtual reality (VR) but also in crucial healthcare applications. The potential for this technology is immense; it could empower individuals with visual impairments to 'feel' their environment or provide essential feedback for users of prosthetic limbs, enhancing their interaction with the world around them.
From Concept to Reality: Building on 'Epidermal VR'
Leading the charge in this technological advancement is John A. Rogers, a trailblazer in bioelectronics at Northwestern. His latest research, showcased in the journal Nature, extends the concept of 'epidermal VR,' a pioneering system introduced in 2019. This earlier work demonstrated how miniature vibrating actuators could communicate touch across large areas of the skin with rapid wireless control.
“Our latest miniaturized actuators surpass the basic 'buzzers' utilized in our initial studies," Rogers explained. "These advanced devices can apply controlled forces over varying frequencies, maintaining a constant force without relying on a continuous power source. Furthermore, some actuators can gently twist at the skin's surface, adding a rich layer of realism to the sensations we can convey.”
A Collaborative Effort
Rogers collaborated with fellow Northwestern professor Yonggang Huang, along with researchers Hanqing Jiang from Westlake University and Zhaoqian Xie from Dalian University of Technology in China. Jiang’s team developed the intricate modifications necessary for the twist motion, further diversifying the haptic feedback options available through this new device.
Harnessing Skin-Stored Energy for Efficiency
This cutting-edge technology features a hexagonal arrangement of 19 tiny magnetic actuators encased in a thin silicone mesh. Each actuator can manifest different sensations such as pressure, vibration, and twisting. With the aid of Bluetooth connectivity to a smartphone, the device processes data about a user's surroundings, translating them into tactile feedback—effectively converting sensory signals like vision into touch.
Notably, while the device operates on a small battery, it incorporates a smart 'bistable' design that conserves energy. This design allows the actuators to exist in two stable positions without a constant energy draw. When actuators exert pressure, they absorb and store energy, which is released when they return to their original position. This energy-efficient mechanism significantly extends the device's operating time on a single battery charge.
The Future is Tactile
As this haptic patch technology evolves, it opens new doors for immersive experiences and practical applications, potentially revolutionizing how we interact with both digital environments and the physical world. With ongoing advancements in wearable tech, the future promises sensations that will not only enhance entertainment but also improve the quality of life for many, turning science fiction into reality one touch at a time.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)