Revolutionary Framework Combines Mobile and Remote Sensing Data to Create Accurate Population Maps!
2024-10-29
Author: Sarah
In a groundbreaking advancement for urban planning, a research team from the Department of Geography at SUNY Buffalo has forged a powerful framework that utilizes a combination of 34 sophisticated models to accurately map monthly population distributions at an unprecedented resolution.
By seamlessly integrating mobile phone data with information on building areas and detailed categories of residential properties, they have developed highly reliable population maps that could change the face of urban studies.
Innovative Modeling Techniques
The standout model employed ordinary least squares (OLS) regression, which effectively merged mobile phone location data with a comprehensive classification system for buildings, including types such as single-family homes and mixed-use residential structures.
Impressively, this model achieved a remarkable accuracy score (R² = 0.82), allowing it to capture monthly fluctuations in population numbers with exceptional precision.
Implications for Urban Planning
This innovative approach provides urban planners and researchers with a practical and replicable tool for meticulously tracking changes in population dynamics.
The pivotal study reached publication on August 23, 2024, in the esteemed Journal of Remote Sensing—a testament to its relevance in contemporary urban geography.
Advancements in Remote Sensing Technologies
By harnessing advanced remote sensing technologies, including LiDAR and Landsat 8 imagery, the framework meticulously maps building areas and vegetation cover, enhancing spatial detail even further.
An analysis of various models revealed that building area emerges as a critical variable influencing population distribution.
Additionally, researchers explored machine learning models to elevate the accuracy of predictions relating to population trends.
Insights from Researchers
"This framework represents a novel solution for understanding urban population dynamics.
By fusing mobile data with remote sensing, we can now create monthly population maps that not only provide higher accuracy but are also timely—essential for effective urban planning and disaster management," remarked Le Wang, co-author of the study and a professor at SUNY Buffalo's Department of Geography.
Methodology and Results
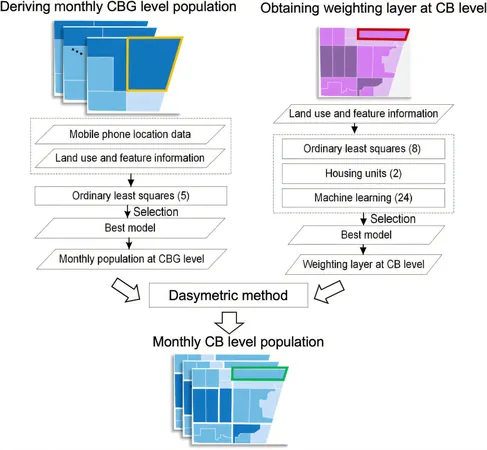
The methodology employed in the research involved a two-phase hybrid approach.
Initially, mobile phone data was assimilated with various population-related variables to refine population estimates at the census block group (CBG) level.
Subsequently, a weighted model layer was generated using advanced statistical and machine learning techniques, honing population data down to the more localized census block (CB) level.
Rigorous model validation, conducted through random sampling, underscored the high accuracy of the results, reinforcing the framework’s reliability with an R² value of 0.82.
Future Prospects
The potential applications for this hybrid approach are vast, as it can readily be utilized to monitor population changes across myriad urban environments.
Looking ahead, there are exciting prospects for widening the model's scope to encompass larger geographic areas and integrate additional real-time data sources, such as traffic patterns and public service usage, to further enhance prediction accuracy and scalability.
This could prove invaluable for city management, emergency response, and informed policy-making, offering deeper and more current insights into urban populations.
With this revolutionary framework, the future of urban planning just got a major technological boost—will this change the way cities are managed forever? Stay tuned!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)