Revolutionary Fractional-Order Model Reveals Monkeypox Dynamics Like Never Before!
2025-08-08
Author: Nur
Monkeypox: A Growing Global Threat
Monkeypox, previously known as monkeypox, is a zoonotic viral disease stemming from the monkeypox virus (MPXV), part of the Orthopoxvirus genus. Discovered in captive monkeys in Denmark in 1958 and first affecting humans in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 1970, monkeypox was traditionally confined to Central and West Africa. However, alarming outbreaks in non-endemic areas have recently triggered global concern.
In May 2022, a multi-country outbreak erupted, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. The outbreak primarily impacted men who have sex with men (MSM), pointing to close physical contact as a key transmission route.
As of December 2023, over 92,000 confirmed cases and 171 deaths across 116 countries have been reported.
Transmission: How Monkeypox Spreads
Monkeypox spreads through animal-to-human and human-to-human routes. Contact with infected animals' blood, fluids, or lesions constitutes a primary transmission vector, with rodents and primates as potential reservoirs. Human-to-human transmission occurs primarily through respiratory droplets during prolonged face-to-face interactions and direct contact with infectious lesions or contaminated items.
Clinical Presentation and Public Health Response
Monkeypox symptoms resemble smallpox but are generally milder. The incubation period spans 5 to 21 days, followed by a phase marked by fever, lymphadenopathy, and other flu-like symptoms. The characteristic centrifugal rash progresses through various stages before crusting and resolving within 2-4 weeks. While typically self-limiting, severe cases can pose risks, especially to children, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals.
In response to the monkeypox outbreak, health interventions have intensified globally, including the revision of vaccination strategies—utilizing smallpox vaccines like the Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) for at-risk populations and post-exposure prophylaxes to reduce severity.
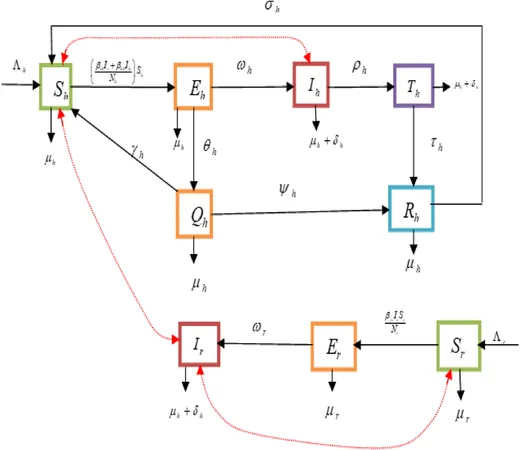
Cutting-Edge Modeling: The Atangana-Baleanu Caputo Fractional Derivative
To better understand monkeypox transmission dynamics, researchers have turned to fractional-order mathematical models, specifically the Atangana-Baleanu Caputo (ABC) operator. This innovative approach incorporates 'memory effects' into disease modeling, capturing complexities that traditional models overlook.
The ABC fractional derivative provides insights into diseases with long incubation periods and slow progression, like monkeypox, offering better predictive power. This modeling technique stabilizes irregularities arising from multifactorial influences, such as fluctuating transmission rates and varying public health interventions. By incorporating historical data, the ABC model yields more realistic simulations, enhancing decision-making capabilities.
Implications for Public Health Policy
The ABC fractional derivative allows public health officials to understand the long-term impact of interventions on monkeypox transmission dynamics. It effectively simulates scenarios like delayed vaccinations and treatment adherence, essential for crafting robust public health strategies.
Crucially, this study emphasizes the need for increased vigilance against monkeypox, combining innovative modeling with rigorous data analysis to formulate effective control measures.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the use of fractional derivatives shows promise, challenges remain regarding the mathematical complexity and practical implementation of these models in real-time decision-making. Future research must explore additional influencing factors and refine sensitivity analyses to enhance the model’s realism and applicability.
In conclusion, the integration of the Atangana-Baleanu Caputo operator into monkeypox dynamics modeling presents a groundbreaking opportunity to tackle this evolving threat, ensuring public health policies are informed by comprehensive and nuanced data.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)