Revolutionary Findings: How Ofloxacin Impacts the Growth of Rana Nigromaculata!
2025-09-05
Author: Siti
Groundbreaking Research Unveils Stereoselective Effects of Ofloxacin on Tadpoles
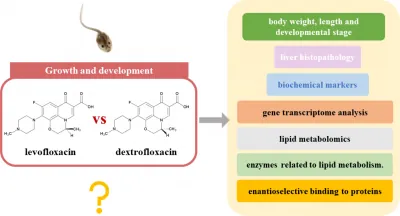
Exciting new research out of Hohai University has revealed startling insights into how the antibiotic ofloxacin affects the development of the black-spotted pond frog, Rana nigromaculata. Published in the *Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering*, this study shines a spotlight on the often-overlooked impact of chiral antibiotics in our environment.
Chirality Matters: The Shocking Truth About Ofloxacin and Levofloxacin
The study showed that when tadpoles were exposed to just 1 µg/L of ofloxacin and its enantiomer levofloxacin over a 75-day period, the results were striking. Levofloxacin had a significantly more detrimental effect on the tadpoles' growth, body length, and overall development compared to dextrofloxacin. This stereoselectivity highlights a crucial insight: the different molecular structures of these drugs can lead to radically different biological effects.
Delving Deeper: Insights from Transcriptomics and Metabolomics
Using advanced transcriptomic analysis, researchers discovered that the differences in gene expression between ofloxacin and levofloxacin were predominantly related to immune responses. Coupled with targeted metabolomics, the findings indicated that the specific impacts on lipid metabolism were due to variations in key lipid compounds within the tadpoles. Notable metabolites included unique phospholipids and triglycerides that reveal the underlying biochemical disruptions caused by ofloxacin.
A Call to Action: Understanding Chiral Antibiotics' Ecological Risks
This study not only enhances our understanding of antibiotic impacts on amphibians but also raises alarming concerns about ecological risks associated with chiral antibiotics in aquatic environments. The selective binding of these enantiomers to enzymes involved in lipid metabolism underscores the need for a more nuanced approach to evaluating the risks posed by such pharmaceuticals.
As research progresses, the findings provide both theoretical and practical frameworks for addressing the ecological threats of antibiotics. With the rise of antibiotic resistance and environmental pollution, understanding these complex interactions is more crucial than ever!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)