Revolutionary Fiber-Optic Technology Enhances Hydrogen Detection
2025-06-23
Author: Yu
A Game-Changer in Hydrogen Sensing Technology
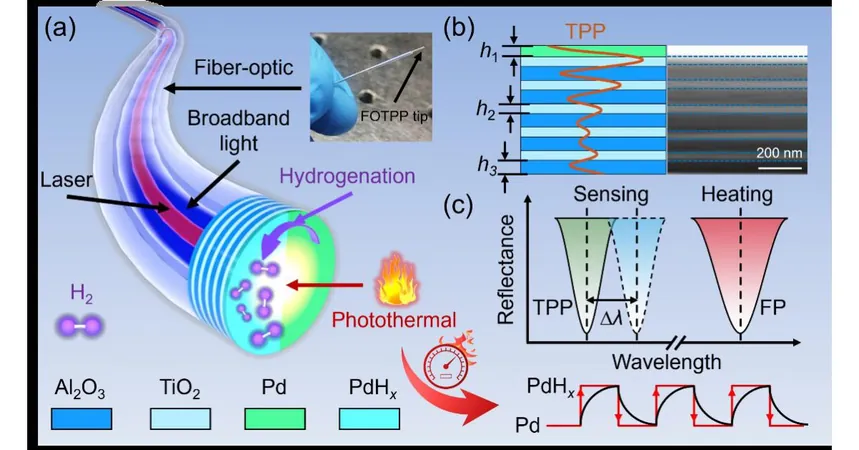
In a groundbreaking development, researchers from Dalian University of Technology and Nanjing University have unveiled a state-of-the-art fiber-optic Tamm plasmon polariton (TPP) tip for hydrogen detection. This innovative system integrates a photothermal approach to amplify sensitivity and response times, marking a significant leap forward in the field.
Why Hydrogen Is the Fuel of the Future
Hydrogen is rapidly becoming the preferred alternative to fossil fuels due to its clean-burning properties and high efficiency. However, its inherent risks—namely, flammability and explosiveness—underscore the urgent need for reliable hydrogen detection systems to ensure safety during widespread use.
The Drawbacks of Traditional Sensors
Currently, conventional hydrogen sensors like Fabry-Pérot and Mach-Zehnder interferometers face considerable hurdles, including complicated fabrication processes. These challenges have hindered their practical applications in real-world situations. In contrast, fiber-optic sensors are gaining traction thanks to their safety features and ability to operate remotely, making them an attractive option for hydrogen detection.
Unleashing the Power of Tamm Plasmon Polaritons
The new TPP-based sensor works by harnessing localized field enhancement effects, vastly improving detection sensitivity compared to conventional methods. Its resonance structure can be easily produced through thin-film deposition, facilitating simpler and cost-effective manufacturing. This approach paves the way for next-gen fiber-optic hydrogen sensors.
A Breakthrough in Performance
The research team, guided by Associate Professor Yuzhang Liang and Professor Wei Peng, has achieved remarkable advancements by introducing a multi-resonance-coupled TPP probe. This design not only boosts detection sensitivity but also accelerates response time significantly, opening new avenues in hydrogen detection technology.
How It Works
By leveraging TPP's local field enhancement, the sensor demonstrates extraordinary sensitivity to hydrogen. The high-absorption resonance enhances the photothermal catalytic effects, dramatically speeding up the detection process. This novel dual enhancement mechanism ensures that even minor changes in hydrogen concentration are detected swiftly.
Superior Performance Metrics
The research indicates that the response speed of this new sensor is 6.5 times faster, and the recovery speed is 2.1 times faster compared to non-resonant conditions, setting new standards in the realm of hydrogen detection.
Looking Ahead
With its unique sensing mechanism and easy-to-manufacture structure, this fiber-optic TPP hydrogen sensor not only presents innovative solutions for the energy sector but also extends the applicability of low-cost multilayer photonic structures in various fields.
The Team Behind the Innovation
The research team continues to push the boundaries of plasmonic structures, focusing on optical manipulations and advanced optoelectronic devices. Their impressive track record includes over 200 publications and collaboration with leading tech companies, ensuring that the findings will have a profound impact on future applications.
A Future Full of Possibilities
As this revolutionary sensor technology reaches its full potential, it promises to create safe environments for hydrogen use, paving the way for a sustainable energy future.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)