Revolutionary Discovery: Targeting MondoA–TXNIP to Ignite Anti-Tumor Immunity in Suppressive Environments
2025-08-22
Author: Yu
Unlocking the Secrets of Immunity Enhancement
Recent groundbreaking research reveals an innovative approach to combat the immunosuppressive microenvironment created by excess lactic acid in tumors. Targeting the MondoA–TXNIP axis may hold the key to revitalizing the body's natural defenses against cancer.
The Impact of Lactic Acid
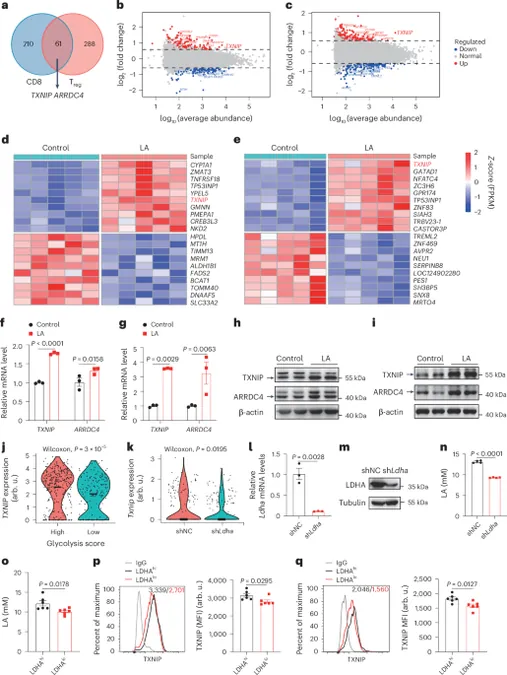
Lactic acid, commonly produced during metabolic processes, has been shown to contribute to a suppressive tumor environment. Investigations into CD8+ T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) demonstrated that lactic acid alters gene expression significantly, dampening anti-tumor activity.
Promising Experimental Findings
Using flow cytometric analysis and QPCR techniques, researchers identified pivotal changes in immune responses following manipulation of the MondoA protein. Notably, enhancing MondoA activity revitalized CD8+ T cells' ability to thrive and combat tumors effectively.
A Double-Edged Sword: Balancing T Cells and Tregs
The findings suggest that in a high lactic acid environment, increasing TXNIP and ARRDC4 expression through MondoA activation can tip the balance between the aggressive CD8+ T cells and the suppressive Tregs. This shift is crucial for amplifying anti-tumor immune responses.
Potential Transformations in Cancer Treatment
This research not only exposes the intricate interplay between various immune cells in the tumor microenvironment but also proposes a tantalizing therapeutic avenue. By targeting the MondoA–TXNIP pathway, treatments could potentially enhance glycolytic activity and elevate the cytotoxic effectiveness of CD8+ T cells.
Conclusion: A New Frontier in Immunotherapy
As we venture into the next era of cancer therapy, focusing on the MondoA–TXNIP axis offers a promising strategy to restore immune function and outsmart cancer's evasive maneuvers. This pioneering research sets the stage for potential breakthroughs that could reshape treatment protocols and improve patient outcomes.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)