
Revolutionary Discoveries: How Deflected Dikes are Transforming Our Understanding of Volcanic Systems
2025-04-11
Author: Mei
Groundbreaking Insights into Volcanic Behavior
In an exciting new study published in AGU Advances, researchers are redefining how we understand magma transport in volcanic systems. They dive into the interactions between rocks and gases, unveiling how complex physical models must capture the dynamism of these geological processes. The challenges amplify when considering eruptions influenced by variable and unpredictable conditions under the Earth’s crust, shaped by its rich volcano-tectonic history.
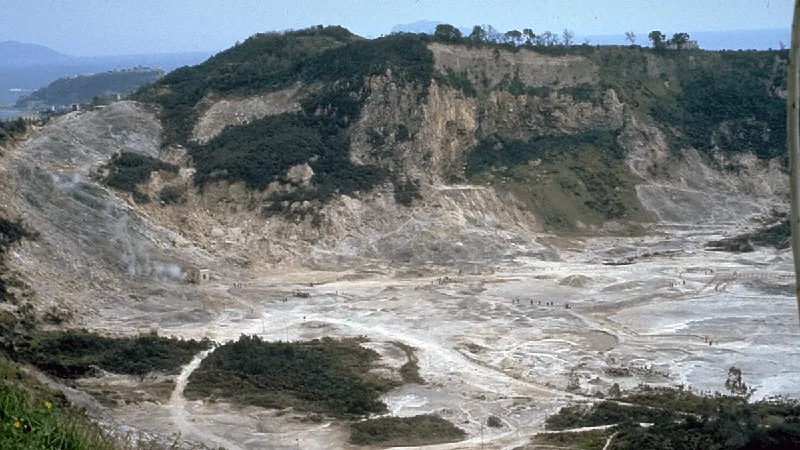
The Campi Flegrei Enigma Unraveled
Focusing on Campi Flegrei in Italy—one of the most notorious volcanic fields—the researchers, led by Buono et al., conducted a comprehensive review that interlaces rock physics, seismic tomography, and mechanical modeling. Their findings propose that the unique combination of caldera shape and rock composition creates a stress state in the crust, affecting how volcanic dikes rise. This process could significantly influence crustal deformation and the pathways for magma and gas, suggesting a critical role for a fragile crustal layer.
A Glimpse into the Future of Volcanology
This research is not just about understanding Campi Flegrei but also sets the stage for more accurate volcanic hazard forecasts worldwide. By harnessing well-instrumented volcanic systems, scientists can create advanced models that integrate real-time observations for more reliable predictions. As the study indicates, while many interactions are yet to be thoroughly explored, the potential for a unified model that could revolutionize our forecasting capabilities is tantalizingly close.
Implications for Global Volcanic Monitoring
With findings that could reshape future volcanic research, this study signals a promising trajectory for understanding magma systems. Advances in technology and interdisciplinary approaches offer hope not only for monitoring volcanoes like Campi Flegrei but for improving safety measures in populations living in volcanic regions globally.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
As researchers continue to delve deeper into the complexities of volcanic systems, the integration of advanced modeling and observational data stands poised to make significant strides in our ability to predict and mitigate volcanic hazards. The journey into the heart of volcanoes like Campi Flegrei has just begun, and the scientific community is abuzz with the possibilities of what lies ahead.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)