Revolutionary Ceramic Material Transforms Electrocaloric Cooling Technology!
2024-11-13
Author: Wei
Introduction
In an exciting breakthrough, researchers have unveiled a novel ceramic material that enhances electrocaloric (EC) cooling, providing an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cooling methods.
Unlike standard vapor-compression cooling systems, which rely heavily on chemical refrigerants, this innovative approach utilizes electric fields to create a cooling effect.
Research Background
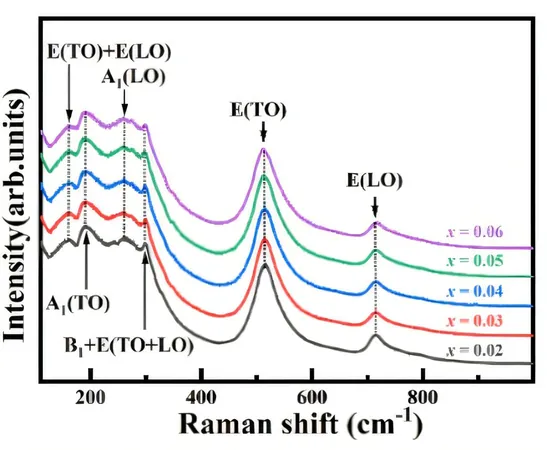
Led by Associate Professor Yin Lihua from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science within the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the research team has focused their efforts on improving the electrocaloric effect in barium titanate (BaTiO3), a material widely utilized in electrocaloric cooling systems.
Their findings, recently published in *Applied Physics Letters*, highlight a groundbreaking method that leverages lattice disorder—a phenomenon traditionally seen as a disadvantage—to enhance the performance of cooling materials.
Methodology and Findings
The team engineered a new ceramic compound, designated BaTi1-x-ySnxZryO3, by strategically combining various elements to induce both size disorder and structural variations within the material.
This creative approach led to significant improvements in the electrocaloric effect, with tests demonstrating an excellent temperature reduction of approximately 0.80 Kelvin when exposed to an electric field.
Real-World Applications
What makes this discovery particularly promising is the material's ability to maintain a substantial cooling effect across a broad temperature spectrum.
This characteristic is vital for real-world applications in diverse cooling devices, from everyday household appliances to advanced electronics.
Conclusion
The key to their success lies in the precise control of lattice disorder and structural composition.
By manipulating these factors, the researchers have achieved stronger and more efficient electrocaloric effects, paving the way for innovations in sustainable cooling technologies.
As the world increasingly shifts towards eco-friendly solutions, this pioneering research not only represents a significant advancement in cooling technology but could also lead to dramatic reductions in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in the future.
Stay tuned as we continue to follow this groundbreaking research and its potential impacts on global cooling systems!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)