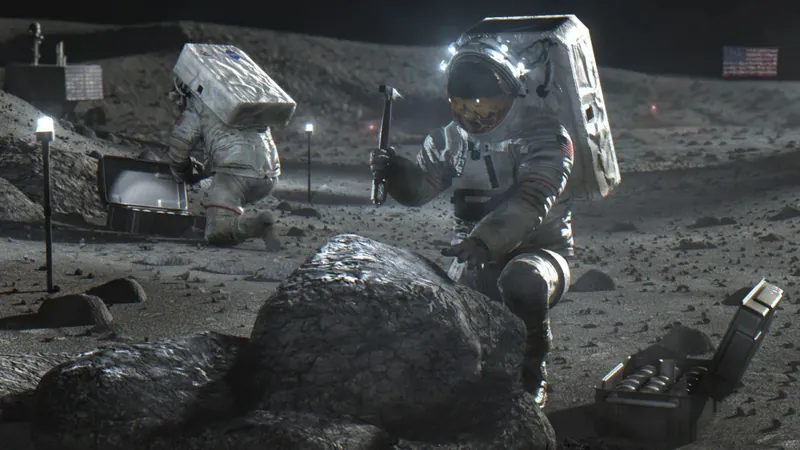

Revolutionary Breakthrough: How Scientists Plan to Generate Oxygen on the Moon!
2025-01-24
Author: Li
Introduction
In a groundbreaking endeavor, engineers are pushing the limits of innovation to create oxygen directly on the Moon. Inside a massive dome-like structure at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, a group of determined scientists has engineered a cutting-edge machine designed to replicate the conditions of lunar regolith— the dusty, abrasive material found on the Moon's surface.
The Experiment
The team's experiment commenced with their unique contraption consuming a small sample of simulated lunar soil. By heating this regolith mixture to staggering temperatures exceeding 1,650°C and mixing in specific reactants, they successfully extracted oxygen molecules! “We’ve completed extensive tests on Earth, and now we’re ready to take the next leap—testing on the Moon!” says Brant White, program manager at Sierra Space, a private space technology firm.
Importance of Oxygen for Lunar Missions
As plans unfold for establishing a lunar base for astronauts, the demand for oxygen becomes critical not just for breathing but also for producing rocket fuel for missions to destinations like Mars. This dual-purpose design could significantly reduce mission costs, with experts estimating it could save billions of dollars compared to transporting oxygen from Earth.
Challenges of Extraction
The lunar soil, rich in metal oxides, presents a treasure trove of resources. Yet the complexities of extracting oxygen on the Moon cannot be understated, particularly due to the unique environmental conditions. The vacuum and extreme temperatures simulated during the recent tests allowed engineers to refine their machinery to withstand the challenging lunar environment.
Adapting to Low Gravity
However, one major obstacle that remains is lunar gravity, which is only one-sixth that of Earth. The extraction processes that rely on gravity, such as those used in traditional electrolysis, face potential delays as the oxygen bubbles may struggle to detach from their electrodes in low-gravity conditions.
Innovative Solutions
Paul Burke from Johns Hopkins University highlights the crucial nature of adapting these technologies: 'If we can overcome lunar gravity issues, we could unlock the moon’s potential for sustainable human exploration.' Innovative solutions, such as utilizing vibrations or modifying electrode designs, could revolutionize how resources are extracted.
The Carbothermal Process
Unlike other methods, Sierra Space’s carbothermal process enables oxygen bubbles to form freely, evading the limitations imposed by electrodes. This technology could be game-changing for future lunar expeditions, with estimates suggesting each astronaut will require around 2-3 kilograms of processed regolith per day for their oxygen needs. However, through advanced life support systems, this amount could be reduced through efficient recycling.
Broader Implications
The implications of generating resources on the Moon extend far beyond oxygen. Researchers are exploring the extraction of essential metals such as iron, titanium, and lithium, which could support 3D printing of spare parts and structures on the lunar base. Palak Patel, a PhD student at MIT, has designed an experimental system that tackles low gravity challenges through the use of sound waves to dislodge oxygen bubbles—potentially unlocking further capabilities for lunar construction!
Advancements in Material Science
Moreover, Patel’s research on melting simulated regolith has led to the formation of robust glass-like materials that could be fashioned into building blocks, paving the way for durable lunar habitats.
Conclusion
With various companies and teams racing to unlock the Moon's riches, the future shines bright for lunar exploration. As we pursue the dream of establishing a human presence on the Moon, these groundbreaking technologies may very well redefine the boundaries of space travel and settlement. Get ready—our celestial neighbor is about to become a hub of activity and innovation unlike anything we've seen before!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)