
Revolutionary AI Supercomputer Set to Transform Alzheimer's Research and More
2025-01-20
Author: Li
Revolutionary AI Supercomputer Set to Transform Alzheimer's Research and More
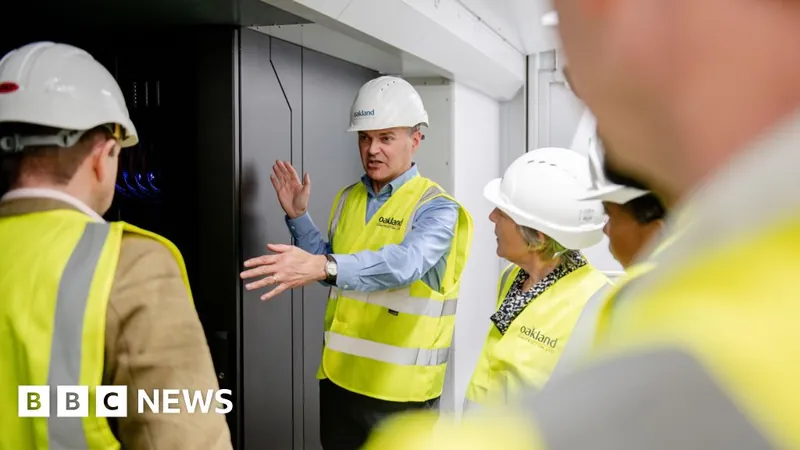
A groundbreaking £225 million supercomputer, known as Isambard-AI, is poised to revolutionize the development of drugs and vaccines, including those targeting Alzheimer's disease. Once fully operational this summer, Isambard-AI will be the most powerful supercomputer in the UK, located at the National Composites Centre in Emersons Green, Bristol.
During a recent announcement, Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer highlighted plans to "unleash AI" across the UK, aiming to drive economic growth and innovation. Simon McIntosh-Smith, a leading professor in high-performance computing at Bristol University, expressed optimism about the UK’s competitive edge in global research thanks to this computing powerhouse.
Currently, parts of the Isambard-AI system are already operational, with researchers using its extensive capabilities to identify new drugs and vaccines. The supercomputer is not only focused on Alzheimer's but also on treatments for heart disease, emphysema, and various cancers. Notably, one research group is enhancing the detection of melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer, across diverse skin tones, which could significantly impact early diagnosis and treatment.
But how does AI facilitate this groundbreaking work? According to Prof. McIntosh-Smith, modern AI models can simulate the intricate interactions of drugs within the body at the molecular level. This process is critical as many medications target specific proteins, altering their behavior to combat diseases. Traditionally, scientists would rely on a mix of experience and guesswork to understand how potential therapies might interact with these proteins. Now, Isambard-AI changes the game by leveraging vast databases of millions of possible drugs, enabling early-stage testing without the need for costly physical experiments.
Instead of testing every possible combination, the AI narrows down the most promising candidates by examining varied options and honing in on those with the highest potential for success. This cutting-edge approach could be instrumental in saving millions of lives and is groundbreaking work being conducted in Bristol.
In addition to medical advancements, Sir Keir Starmer emphasized the broader transformative potential of AI in public services, suggesting applications ranging from pothole detection on roads to faster cancer diagnoses. Prof. McIntosh-Smith likened the significance of AI development to the introduction of the internet and mobile phones, underlining the public benefit of government-funded initiatives compared to those pursued strictly in corporate contexts.
While concerns about energy consumption have arisen due to the rapid escalation of AI technology, Isambard-AI is designed with efficiency in mind. Interestingly, the supercomputer produces waste energy in the form of hot water, which the team plans to explore as a resource for heating local homes and businesses.
With Isambard-AI expected to rank among the world's top 10 fastest supercomputers, the world watches eagerly as it pioneers advancements in healthcare and sustainability, potentially redefining our approach to disease and community energy solutions. Stay tuned for updates on this exciting venture that signifies a new dawn in medical research and public resource management!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)