Revolutionary AI Model Transforms Atrial Fibrillation Treatment: Who Really Needs Blood Thinners?
2025-09-01
Author: Jia
Groundbreaking AI Identifies Blood Thinner Necessity for Atrial Fibrillation Patients
In a remarkable breakthrough, researchers at Mount Sinai have devised an innovative artificial intelligence model that could redefine how atrial fibrillation (AF) patients are treated concerning anticoagulants—commonly prescribed blood thinners essential for stroke prevention. This game-changing study was presented at the European Society of Cardiology, showcasing a cutting-edge method that could significantly impact patient care worldwide.
The Heart of the Matter: Atrial Fibrillation's Global Impact
Atrial fibrillation is the most prevalent irregular heart rhythm, affecting around 59 million people globally. This condition causes the heart's upper chambers to tremble, which can lead to blood stagnation and clot formation, ultimately increasing the risk of strokes. While blood thinners are typically prescribed to prevent such events, they come with their own risks, including potentially severe bleeding—raising the crucial question of who truly needs them.
AI-Powered Personalization: A Game Changer for Patients
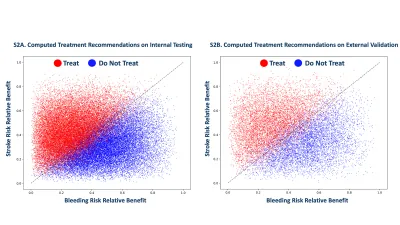
The revolutionary AI model developed by Mount Sinai stands out by offering tailored treatment recommendations based on comprehensive electronic health records of individual patients. Unlike traditional methods, which rely on population averages to assess risk, this AI considers a patient’s unique clinical features, weighing the likelihood of stroke against the potential for major bleeding. This personalized approach could mean that nearly half of AF patients who would typically receive blood thinners might not necessarily need them, fundamentally shifting treatment paradigms.
A Deep Dive Into the Study's Methodology and Findings
Trained on a staggering dataset of 1.8 million patients spanning over 21 million doctor visits, the AI model produces precise recommendations after analyzing approximately 1.2 billion data points. Validation included a study of 38,642 AF patients within Mount Sinai and an external assessment with data from 12,817 additional patients. The findings demonstrated a significant reclassification, with many patients deemed unnecessary for anticoagulation treatment under this new model.
Empowering Patients and Clinicians: A New Era in Healthcare
This pioneering study not only heralds a new approach to treating atrial fibrillation but also represents a monumental leap in personalized medicine. By creating an individualized risk profile, this AI system empowers clinicians to make informed, data-driven decisions regarding patient care, ultimately enhancing outcomes. It helps address the common patient question: "What does this mean for me?" providing clearer insights into individual health scenarios.
Expert Insights: What This Means for Future Healthcare
Prominent figures in the study assert that this model embodies a modernization of anticoagulation management for AF patients. Dr. Joshua Lampert, the study's lead author, highlights how it alleviates the burden on clinicians to extrapolate from population-level data, allowing for real-time adjustments to treatment recommendations based on a patient’s evolving health status. As emphasized by Dr. Vivek Reddy, the goal remains clear: avoiding stroke is paramount for those battling AF.
Mount Sinai: Leading the Charge in Cardiovascular Care
Renowned for its excellence, the Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital is positioned as a leader in the field of cardiology, consistently ranked among the best in the nation and worldwide. As part of a vast network dedicated to pioneering research and providing high-quality care, this new AI-driven approach adds another layer to their commitment to patient safety and effective treatment.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)