Revolutionary AI Model Set to Transform Mammography for Early Breast Cancer Detection
2025-05-21
Author: Yu
A groundbreaking model leveraging deep learning algorithms could revolutionize the way mammography detects breast cancer, particularly for women facing preliminary BI-RADS 3 and 4 classifications.
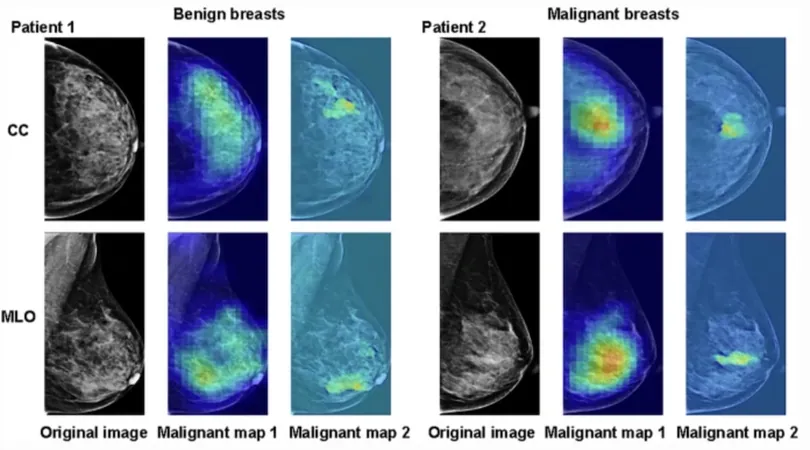
Published in the journal Insights into Imaging, the innovative convolutional neural network (CNN) model employs a two-step process that pinpoints malignant lesions at a patch level and performs mammography image-level classification. This ambitious study analyzed data from over 12,000 Asian women.
Remarkably, the AI model achieved Area Under the Curve (AUC) scores of 93.3% and 94.7% in detecting malignant lesions across two testing groups. On average, it demonstrated an impressive sensitivity of 82.6%, specificity of 95.5%, and an overall accuracy of 93.1%.
What’s more, in cases with initial BI-RADS 3 and 4 assessments, the AI system successfully downgraded a staggering 83.1% of false-positive cases to benign classifications and identified 54.1% of false-negative cases as malignant.
Lead researcher Dr. Hongna Tan, from the Henan Provincial People's Hospital, underscored the model's clinical relevance: "This AI system could serve as a vital tool for identifying malignancy on mammograms, aiding in decision-making within the BI-RADS framework and minimizing risks of over-diagnosis and delays in treatment."
The study highlights a striking improvement in specificity, with AI model results reaching between 90.5% and 96.3% in validation cohorts—significantly outpacing initial BI-RADS assessments, which fell between 58.8% to 74.3%.
### Key Insights from the Study:
1. Superior Diagnostic Performance
The deep learning model displayed exceptional performance metrics, achieving high AUC values of 93.3% and 94.7%, coupled with 82.6% sensitivity and 95.5% specificity.
2. Enhanced BI-RADS Stratification
The innovative model effectively refined BI-RADS classifications, reducing false positives and improving the categorization of cases that initially presented as false negatives.
3. Targeted Clinical Relevance for Asian Populations
By training on a large cohort of women with dense breast tissue, the AI model addresses specific challenges faced by Asian populations, who typically experience higher rates of dense mammary tissue.
Given the low rates of mammography screening in Asia, this AI model could provide significant advantages in early detection for these patients.
Dr. Tan pointed out a critical distinction: "Our model was specifically developed for Asian women, who often exhibit high densities and nuanced lesions on mammograms, unlike previous studies that predominantly focused on Caucasian populations."
While citing limitations, including the underrepresentation of BI-RADS 1 and 2 cases and the use of a single mammography vendor, the authors remain optimistic. This AI innovation holds the promise of transforming breast cancer diagnostics and offers hope for improved patient outcomes.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)