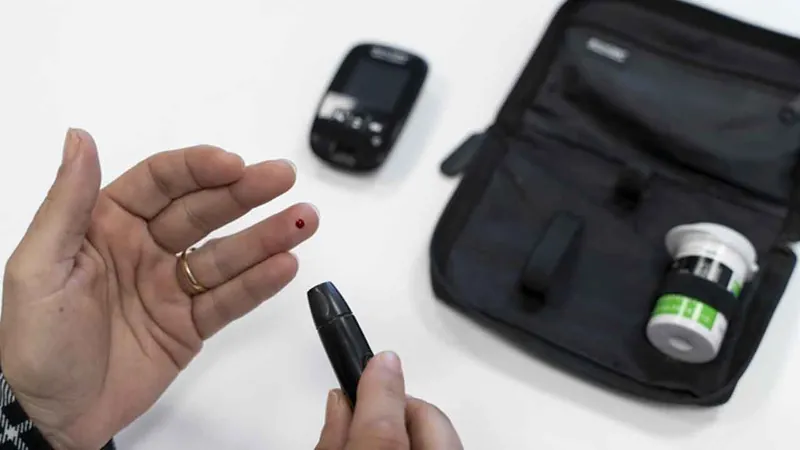

Revolutionary AI Dataset Set to Transform Our Understanding of Diabetes
2024-11-11
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
In a ground-breaking development, scientists from a pioneering study have unveiled a comprehensive AI-driven dataset aimed at unlocking new insights into type 2 diabetes. Conducted in New York, this innovative research focuses on the interplay of biomarkers and environmental factors influencing the onset of the disease.
Diverse Participant Pool
Unlike previous studies, this research incorporates a diverse participant pool, including individuals without diabetes and those at various stages of the condition. Early findings reveal intriguing patterns, suggesting that type 2 diabetes is not a uniform ailment but rather a complex tapestry of individual health experiences. Dr. Cecilia Lee, an esteemed professor of ophthalmology at the University of Washington School of Medicine, remarked, “We see data supporting heterogeneity among type 2 diabetes patients — that people aren’t all dealing with the same thing. With the acquisition of such large and detailed datasets, researchers will have the ability to delve deeply into these differences.”
Environmental Factors
One of the significant elements of the study involves data collected via customized environmental sensors installed in participants’ homes, highlighting a startling correlation between the severity of the disease and exposure to fine particulate pollution—a revelation that could spark further investigations into environmental health impacts.
Comprehensive Dataset
The comprehensive dataset not only encompasses environmental factors but also incorporates survey responses, depression scales, eye imaging scans, and traditional measurements of glucose and biological variables. The researchers aim to leverage artificial intelligence to mine this rich pool of data for groundbreaking insights into risks, preventive strategies, and the interconnectedness of disease and health.
Commitment to Inclusivity
A notable aspect of this study is its commitment to inclusivity; it aspires to gather health information from a more racially and ethnically diverse population than has been previously analyzed. This ensures that the insights derived could have far-reaching implications for a wider demographic, making the data accessible for AI-driven research while upholding ethical standards and data security.
Collaboration and Future Implications
As Dr. Aaron Lee, the principal investigator of the project and fellow professor of ophthalmology at UW Medicine, expressed, “This process of discovery has been invigorating. We are a consortium of seven institutions, bringing together multidisciplinary teams that had not collaborated prior. Our shared goal is to utilize unbiased data while ensuring the security of that information, making it available to colleagues worldwide.”
Conclusion
As the research progresses, the implications may well pave the way for revolutionary changes in how we understand, prevent, and treat type 2 diabetes. Stay tuned as these findings could reshape future health policies and individual approaches to this prevalent condition!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)